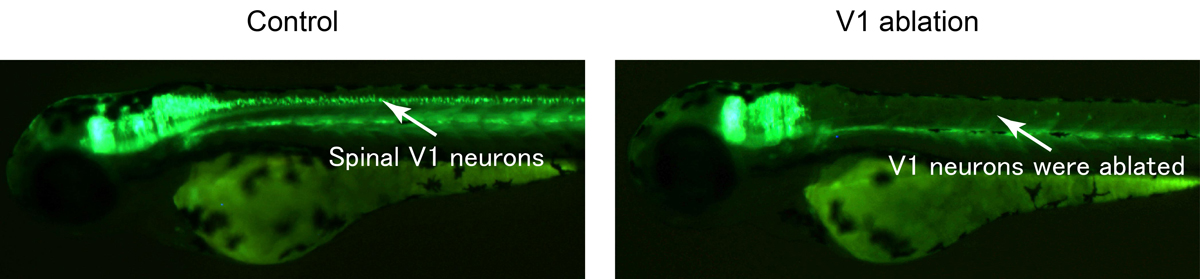
In vertebrate muscles, there are slow and fast muscle fibers. Fast muscle fibers contract rapidly, but are prone to fatigue. Slow muscle fibers have the property of slow contraction, but resist to fatigue. Vertebrates use fast and slow muscles properly depending on the situation. Using zebrafish larvae, Assistant Professor Yukiko Kimura and Professor Shin-ichi Higashijima of the National Institute for Basic Biology in Japan have discovered neural mechanisms that suppress slow muscle activity in fish swimming at high speeds. The research results were published in the May 22, 2019 issue of
Nature Communications.