Kamei Lab. / Laboratory for Biothermology
-Aiming to elucidate the biological significance of heat and temperature-

-Temperature biology-
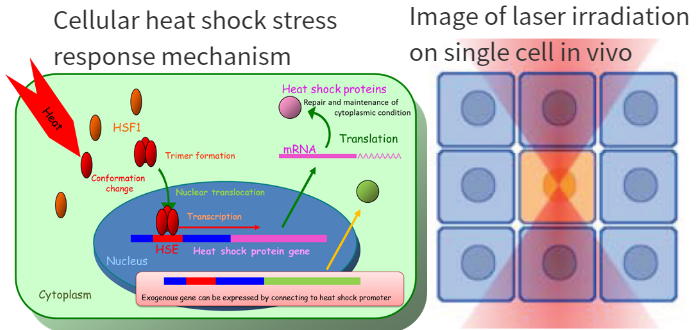

Many organisms have a heat shock response mechanism that protects cells from heat stress (Fig. 1, left). Laboratory for Biothermology is focusing on heat shock transcription factor (HSF) 1 as one means for clarifying the connection between temperature and organisms, and is conducting research to clarify its temperature sensing mechanism and activation kinetics.
Currently, we are working on the elucidation of the molecular mechanism of HSF1 activation from multiple biological species such as medaka, medaka-related species, flounder, and frog from a biological perspective.
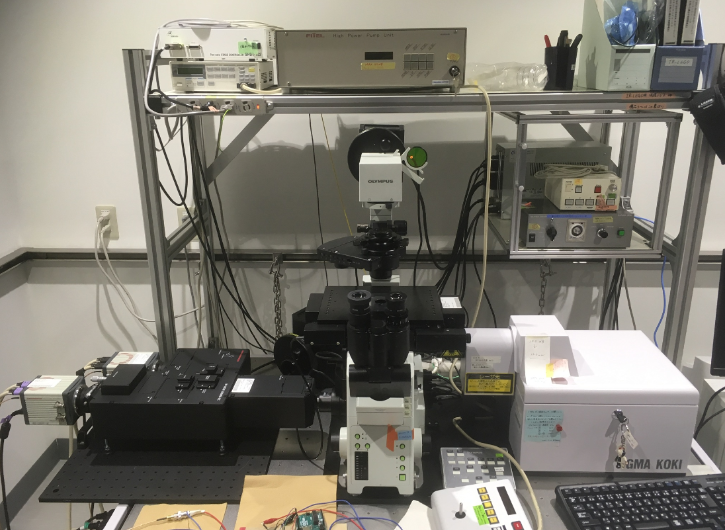
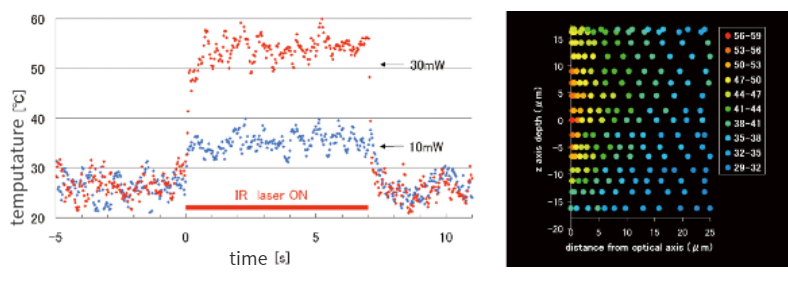
In addition, it is necessary to know the thermophysical properties of biological materials in order to investigate the connection between temperature and living things. Therefore, we are also developing a microscope technology that can measure the temperature of target cells in vivo while heating locally. So far, we have constructed a high-speed living body temperature imaging system (Fig. 2) by applying a fluorescent protein probe (Reference 1) that can measure temperature from the ratio of fluorescence intensity of two wavelengths. Using this, we are trying to analyze thermophysical properties of biological materials.
Reference1. Nakano M., Arai Y., Kotera I., Okabe K., Kamei Y., Nagai T. (2017). Genetically encoded ratiometric fluorescent thermometer with wide range and rapid response. PLoS One, 12(2), e0172344.
-Local gene expression technology and its improvement-
By utilizing the heat shock response and inserting the target gene downstream of the heat shock promoter and introducing it into an organism, it becomes possible to induce the expression of the target gene by heat shock. Laboratory for Biothermology possesses technology that can induce (manipulate) the expression of target genes only by target cells by focusing and irradiating infrared laser with a microscope to heat single cells in the body (Fig. 1, right).
This method (IR-LEGO method: Reference 4) is applied to model organisms such as medaka, zebrafish, and Arabidopsis. Many collaborative studies (references 2 and 3) with researchers outside of Japan are carried out using this technology. On the other hand, the current IR-LEGO has some difficulties. In order to overcome it, we are applying the above research to improve IR-LEGO.
Reference 2. Okuyama, T., Yokoi, S., Abe, H., Isoe, Y., Suehiro, Y., Imada, H., Tanaka, M., Kawasaki, T., Yuba, S., Taniguchi, Y., Kamei, Y., Okubo, K., Shimada, A., Naruse, K., Takeda, H., Oka, Y., Kubo, T. and Takeuchi, H. (2014). A neural mechanism underlying mating preferences for familiar individuals in medaka fish. Science, 343, 91-94.
Reference 3. Shimada, A., Kawasishi, T., Kaneko, T., Yoshihara, H., Yano, T., Inohaya, K., Kinoshita, M., Kamei, Y., Tamura, K. and Takeda, H. (2013). Trunk exoskeleton in teleosts is mesodermal in origin. Nat. Commun., 4, 1639.
Reference 4. Kamei, Y., Suzuki, M., Watanabe, K., Fujimori, K., Kawasaki, T., Deguchi, T., Yoneda, Y., Todo, T., Takagi, S., Funatsu, T., and Yuba, S. (2009). Infrared laser-mediated gene induction in targeted single cells in vivo. Nat. Methods 6, 79-81.(Pubmed)

Associate Professor (Specially appointed)
Assistant Professor (Specially appointed)
CREST Research Fellow
JSPS Research Fellow
Postdoctral Researcher
Technical Assistants
Chie Kinoshita
| Publications |
|---|
| 【2020】 |
| (73) Watanabe, Y.,Okuya, K., Takada, Y., Kinoshita, M., Yokoi, S., Chisada, S., Kamei, Y., Tatsukawa, H., Yamamoto, N., Abe, H., Hashimoto, H. and Hitomi, K. (2020). Gene disruption of medaka (Oryzias latipes) orthologue for mammalian tissue-type transglutaminase (TG2) causes movement retardation. J Biochem. in press. |
| (72) Yokoi, S., Naruse, K., Kamei, Y., Ansai, S., Kinoshita, M., Mito, M., Iwasaki, S., Inoue, S., Okuyama, T., Nakagawa, S., Young, L. J. and Takeuchi, H. (2020). Sexually dimorphic role of oxytocin in medaka mate choice. PNAS 117, 4802-4808. プレスリリース(基礎生物学研究所)(北海道大学) (東北大学)(岡山大学) |
| (71) Fujikawa, Y., Ishikawa-Fujiwara, T., Kuo, T., Shinkai, N., Shoji, T., Kawasaki, T., Kamei, Y., Sakuraba, Y., Sato, A., Kinoshita, M., Gondo, Y., Yuba, S., Tsujimura, T., Sese, J. and Todo, T. (2020). Involvement of Rev1 in alkylating agent-induced loss of heterozygosity in Oryzias latipes. Genes Cells. 25, 124-138. |
| 【2019】 |
| (70) Kosugi, M., Ozawa, S. I., Takahashi, Y., Kamei, Y., Itoh, S., Kudoh, S., Kashino, Y. and Koike, H.(2019) Red-shifted chlorophyll a bands allow uphill energy transfer to photosystem Ⅱ reaction centers in an aerial green alga, Prasiola crispa, harvested in Antarctica, Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg. 1861, 148139. 研究成果(アストロバイオロジーセンター) |
| (69) Abe, G., Hayashi, T., Yoshida, K., Yoshida, T., Kudoh, H., Sakamoto, J., Konishi, A., Kamei, Y., Takeuchi, T., Tamura, K. and Yokoyama, H. (2019). Insights regarding skin regeneration n non-amniote vertebrates: Skin regeneration without scar formation and potential step-up to a higher level of regeneration. Seminars in cell & developmental biology 100,109-121 |
| (68) Ikehata, H., Mori, T., Kamei, Y., Douki, T., Cadet, J. and Yamamoto, M. (2020). Wavelength- and Tissue-dependent Variations in the Mutagenicity of Cyclobutane Pyrimidine Dimers in Mouse Skin. Photochem Photobiol. |
| (67) Nakane, Y., Shinomiya, A., Ikegami, K., Shimmura, T., Higashi, S., Kamei, Y., Yoshimura, T. and Ota, W. (2019). Action spectrum for photoperiodic control of thyroid-stimulating hormone in Japanese quail (Coturnix japonica). PLoS One 14, e0222106 |
| (66) Hwang D, Wada S, Takahashi A, Urawa H, Kamei Y and Nishikawa S. (2019) Development of a Heat-inducible Gene Expression System using Female Gametophytes of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol. pcz148. |
| (65) Uchimura, T., Hara, S., Yazawa, T., Kamei, Y. and Kitano, T. (2019). Involvement of heat shock proteins on the transcriptional regulation of corticotropin-releasing hormone in Medaka. Frontiers in Endocrinology 10, 529 |
| (64) Shikata, T., Takahashi, F., Nishide, H., Shigenobu, S., Kamei, Y., Sakamotomo, S., Yuasa, K.., Nishiyama, Y., Yamasaki, Y. and Uchiyama, I. (2019). RNA-seq analysis reveals genes related to photoreception, nutrient uptake, and toxicity in a noxious red-tide raphidophyte Chattonella antiqua. Frontiers in Microbiology 10, 1764 プレスリリース(基礎生物学研究所)(水産研究・教育機構) |
| (63) Furukawa F, Hamasaki S, Hara S, Uchimura T, Shiraishi E, Osafune N, Takagi H, Yazawa T, Kamei Y & Kitano T. (2019) Heat shock factor 1 protects germ cell proliferation during early ovarian differentiation in medaka. Sci Rep 9(6927) プレスリリース(熊本大学) |
| (62) Nakayama T, Shimmura T, Shinomiya A, Okimura K, Takehana Y, Furukawa Y, Shimo T, Senga T, Nakatukasa M, Nishimura T, Tanaka M, Okubo K, Kamei Y, Naruse K & Yohimura T. (2019) Seasonal regulation of the lncRNA LDAIR modulates self-protective behaviours during the breeding season. Nat Ecol Evol 08(April) プレスリリース(基礎生物学研究所) |
| (61) Abe E, Yasugi M, Takeuchi H, Watanabe E, Kamei Y and Yamamoto H. (2019) Development of omnidirectional aerial display with aerial imaging by retro-reflection (AIRR) for behavioral biology experiments. Optical Review 26, 221-229. |
| (60) Harada Y, Matsuo M, Kamei Y, Goto M, Fukamachi S. (2019) Evolutionary history of the medaka long-wavelength sensitive genes and effects of artificial regression by gene loss on behavioural photosensitivity. Sci Rep. 25, 2726-2736. |
| 【2018】 |
| (59) Amemiya S, Hibino T, Minokawa T, Naruse K, Kamei Y, Uemura I, Kiyomoto M, Hisanaga S and Kuraishi R. (2018) Development of the coelomic cavities in larvae of the living isocrinid sea lily Metacrinus rotundus. Acta Zool., 96(1):36-43. |
| (58) Kosugi M, Maruo F, Inoue T, Kurosawa N, Kawamata A, Koike H, Kamei Y, Kudoh S and Imura S. (2018) A comparative study of wavelength-dependent photoinhibition of drought-tolerant photosynthetic organisms in Antarctica and the potential risks of photo-damage in the habitat. Ann. Bot., 122(7):1263-1278. |
| (57) Hamada T, Yako M, Minegishi M, Sato M, Kamei Y, Yanagawa Y, Toyooka K, Watanabe Y and Hara-Nishimura I. (2018) Stress granule formation is induced by a threshold temperature rather than a temperature difference in Arabidopsis. J. Cell Sci., 131(jcs216051) |
| (56) Matsuo M, Ando Y, Kamei Y and Fukamachi S. (2018) A semi-automatic and quantitative method to evaluate behavioral photosensitivity in animals based on the optomotor response (OMR) Biol Open.,7 bio033175. |
| (55) Tominaga J, Nakahara Y, Horikawa D, Tanaka A, Kondo M, Kamei Y, Takami T, Sakamoto W, Unno K, Sakamoto A and Shimada H. (2018) Overexpression of the protein disulfide isomerase AtCYO1 in chloroplasts slows darkinduced senescence in Arabidopsis. BMC Plant Biol, 18 80 |
| (54) Nagao Y, Takada H, Miyadai M, Adachi T, Seki R, Kamei Y, Hara I, Taniguchi Y, Naruse K, Hibi M, Kelsh RN, Hashimoto H. (2018) Distinct interactions of Sox5 and Sox10 in fate specification of pigment cells in medaka and zebrafish. PLoS Genetics, 4(4) e1007260 |
| (53) Hasugata R, Hayashi S, Kawasumi-Kita A, Sakamoto J, Kamei Y and Yokoyama H. (2018) Infrared laser-mediated single-cell-level gene induction in the regenerating tail of Xenopus laevis tadpoles. Cold Spring Harb Protoc., May 16 10.1101/pdb.prot101014 |

|
| This paper was selected as a cover art. |
| (52) Tonoyama Y, Shinya M, Toyoda A, Kitano T, Oga A, Nishimaki T, Katsumura T, Oota H, Wan MT, Yip BWP, Helen MOL, Chisada S, Deguchi T, Au DWT, Naruse K, Kamei Y, Taniguchi Y. (2018) Abnormal nuclear morphology is independent of longevity in a zmpste24-deficient fish model of Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome (HGPS). Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol , 209, 54-62. |
| (51) Watanabe Y, Furukawa E, Tatsukawa H, Hashimoto H, Kamei Y, Taniguchi Y, Hitomi K. (2018) Higher susceptibility to osmolality of the medaka (Oryzias latipes) mutants in orthologue genes of mammalian skin transglutaminases. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 82,1165-1168. |
| (50) Nakamoto M, Shibata Y, Ohno K, Usami T, Kamei Y, Taniguchi Y, Todo T, Sakamoto T, Young G, Swanson P, Naruse K and Nagahama Y. (2018) Ovarion aromatase loss-of-function mutant medaka undergo ovary degeneration and partial female-to-male sex reversal after puberty. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. , 460:104-122. |
| 【2017】 |
| (49) Ishikawa T, Kashima M, Nagano A J, Ishikawa-Fujiwara T, Kamei Y, Todo T and Mori K. (2017) Unfolded protein response transducer IRE1-mediated signaling independent of XBP1 mRNA splicing is not required for growth and development of medaka fish. eLife, 6 e26845. |
| (48) Shimmura T, Nakayama T, Shinomiya A, Fukamachi S, Yasugi M, Watanabe E, Shimo T, Senga T, Nishimura T, Tanaka M, Kamei Y, Naruse K and Yoshimura T.(2017) Dynamic plasticity in phototransduction regulates seasonal changes in color perception. Nat. Commun., 8412 プレスリリース(基礎生物学研究所) |
| (47) Hattori M, Tamada Y, Murata T, Oya S, Hasebe M, Hayano Y and Kamei Y. (2017) Artificial testing targets with controllable blur for adaptive optics microscopes. Genome Biology Optical Engineering 56(8) 080502. |
| (46) Yasuko Isoe, Ryohei Nakamura, Yasuhiro Kamei, Shigenori Nonaka, Teruhiro Okuyama, Atsushi Shimizu, Takeo Kubo, Hiroyuki Takeda, Hideaki Takeuchi. Clonal analysis of construction mechanism of the adult telencephalon mediated by post-hatch neurogenesiss in medaka fish. Mechanisms of Development, 145 S118. |
| (45) Yoshihiro Morishita, Takayuki Suzuki, Hitoshi Yokoyama, Yasuhiro Kamei, Koji Tamura, Aiko Kawasumi. Quantitative and comparative analysis of tissue deformation dynamics for chick and Xenopus limb morphogenesis. Mechanisms of Development, 145 S40. |
| (44) Ishikawa T, Toyama T, Nakamura Y, Tamada K, Shimizu H, Ninagawa S, Okada T, Kamei Y, Ishikawa-Fujiwara T, Todo T, Aoyama E, Takigawa M, Harada A and Mori K(2017) UPR transducer BBF2H7 allows export of typeⅡ collagen in a cargo- and developmental stage-specific manner. J. Cell Biol., jcb. 201609100. プレスリリース(京都大学) |
| (43) Masayuki Hattori, Yosuke Tamada, Shin Oya, Yutaka Hayano, Yasuhiro Kamei. (2017) Basic experiments of laser beam correcion by adaptive optics microscope for the accurate manipulation of biological tissues. Biomedical Imaging and Sensing Conference |
| (42) Nakano M, Arai Y, Kotera I, Okabe K, Kamei Y & Nagai T. (2017) Genetically encoded ratiometric fluorescent thermometer with wide range and rapid response. PLoS One, 12(2) e0172344. |
| (41) Homma N, Harada Y, Uchikawa T, Kamei Y and Fukamachi S.(2017). Protanopia (red color-blindness) in medaka: a simple system for producing color-blind fish and testing their spectral sensitivity. BMC Genetics, 18(10). |
| 【2016】 |
| (40) Zeng C W, Kamei Y, Wang CT and Tsai H J. (2016). Subtypes of hypoxia-responsive cells differentiate into neurons in spinal cord of zebrafish embryos after hypoxic stress. Biol. Cell 108, 357-377. |

|
| This paper was selected as a cover art. |
| (39) Yokoyama R, Yamamoto H, Kondo M, Takeda S, Ifuku K, Fukao Y, Kamei Y, Nishimura M and Shikanai T.(2016). Grena-localized proteins, RIQ1 and RIQ2, optimize the dynamics of light-harvesting complex Ⅱ and grana stacking in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell, 28, 2261-2275. |
| (38) Utagawa U, Higashi S, Kamei Y, Fukamachi S. (2016). Characterization of assortative mating in medaka: Mate discrimination cues and factors that blas sexual preference. Hormones and Behavior, 84 9-17. |
| (37) Yokoi S, Ansai S, Kinoshita M, Naruse K, Kamei Y, Young LJ, Okuyama T, Takeuchi H. (2016). Mate-guarding behavior enhances male reproductive success via familarization with mating partners in medaka fish. Front Zool., 13(21). |
| (36) Suzuki M, Takagi C, Miura S, Sakane Y, Suzuki M, Sakuma T, Sakamoto N, Endo T, Kamei Y, Sato Y, Kimura H, Yamamoto T, Ueno N, Suzuki K.T. (2016) In vivo tracking of histone H3 lysine 9 acetylation in Xenopus laevis during tail regeneration Gene Cells, 21 358-369. |
| (35) Nishihama, R., Ishida, S., Urawa, H., Kamei, Y. and Kohchi, T. (2016). Conditional Gene Expression/Deletion Systems for Marchantia polymorpha Using its Own Heat-shock Promoter and the Cre/loxP-mediated Site-specific Recombination. Plant Cell Physiol., 27 271-280. |
| 【2015】 |
| (34) Kawasumi-Kita A, Hayashi T, Kobayashi T, Nagayama C, Hayashi S, Kamei Y, Morishita Y, Takeuchi T, Tamura K and Yokoyama H.(2015) Application of local gene induction by infrared laser-mediated microscope and temperature stimulator to amphibian regeneration study. Dev. Growth Differ. , 57(9) 601-613. プレスリリース(基礎生物学研究所) |
| (33) Nakashima M, Suzuki M, Saida M, Kamei Y, Hossain M B and Tokumoto T. (2015) Cell-based assay of nongenomic actions of progestins revealed inhibitory G protein coupling to membrane progestin receptor α (mPRα) Steroids , 100 21-26. |
| (32) Yokoi S, Okuyama T, Kamei Y, Naruse K, Taniguchi Y, Ansai S, Kinoshita M, Young L J, Takemori N, Kubo T and Takeuchi H. (2015). An essential role of the arginine vasotocin system in mate-guarding behaviors in triadic relationships of medaka fish (Oryzias latipes) PLoS Genetics, 11(2) e1005009. |
| 【2014】 |
| (31) Hayashi S, Ochi H, Ogino H, Kawasumi A, Kamei Y, Tamura K and Yokoyama H. (2014). Transcriptional regulators in the Hippo signaling pathway control organ growth in Xenopus tadpole tail regeneration. Dev. Biol. 396 31-41. プレスリリース(基礎生物学研究所) |
| (30) Fang X, Ide N, Higashi S, Kamei Y, Toyooka T, Ibuki Y, Kawai K, Kasai H, Okamoto K, Arimoto-Kobayashi S, Negishi T. (2014) Somatic cell mutations caused by 365 nm LED-UVA due to DNA double-strand breaks through oxidative damage Photochem Photobiol Sci. ,13(9) 1338-1346. |
| (29) Murozumi N, Nakashima R, Hirai T, Kamei, Y, Ishikawa-Fujiwara T, Todo, T and Kitano T. (2014). Loss of follicle-stimulating hormone receptor function causes masculinization and suppression of ovarian development in genetically female medaka. Endocrinology, 155(8) 3136-3145. |
| (28) Tamada Y, Murata T, Hattori M, Oyac S, Hayano Y, Kamei Y and Hasebe M. (2014) Optical Property Analyses of Plant Cells for Adaptive Optics Microscopy. Int. J. Optomechatronics, 8, 89-99. |
| (27) Nagao Y, Suzuki T, Shimizu A, Kimura T, Seki R, Adachi T, Inoue C, Omae Y, Kamei Y, Hara I, Taniguchi Y, Naruse K, Wakamatsu Y, Kelsh R N, Hibi M, Hashimoto H. (2014). Sox5 functions as a fate switch in medaka pigment cell development. PLoS Genet., 10(4):e1004246. プレスリリース (基礎生物学研究所) |
| (26) Otozai S, Ishikawa-Fujiwara T, Oda S, Kamei Y, Ryo H, Sato A, Nomura T, Mitani H, Tsujimura T, Inohara H and Todo T. (2014). p53-Dependent suppression of genome instability in germ cells. Mutat Res. Fundam. Mol. Mech. Mutagen,760:24-32. |
| (25) Okuyama T, Yokoi S, Abe H, Isoe Y, Suehiro Y, Imada H, Tanaka M, Kawasaki T, Yuba S, Taniguchi Y, Kamei Y, Okubo K, Shimada A, Naruse K, Takeda H, Oka Y, Kubo T and Takeuchi H. (2014). A neural mechanism underlying mating preferences for familiar individuals in medaka fish. Science, 343, 91-94. プレスリリース (基礎生物学研究所)(東京大学) |
| 【2013】 |
| (24) Okuyama T, Isoe Y, Hoki M, Suehiro Y, Yamagishi G, Naruse K, Kinoshita M, Kamei Y, Shimizu A, Kubo T and Takeuchi H. (2013). Controlled Cre/loxP site-specific recombination in the reveloping brain in medaka fish, Oryzias latipes. PLoS ONE 8, e66597. |
| (23) Kimura E, Deguchi T, Kamei Y, Shoji W, Yuba S and Hitomi J. (2013). Application of infrared laser to the zebrafish vascular system: gene induction, tracing, and ablation of single endothelal cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol.,33, 1264-1270. プレスリリース(基礎生物学研究所) (岩手医科大学) |
| (22) Shimada A, Kawanishi T, Kaneko T, Yoshihara H, Yano T, Inohaya K, Kinoshita M, Kamei Y, Tamura K and Takeda H. (2013). Trunk exoskeleton in teleosts is mesodermal in origin. Nature Communications., 4, 1639. プレスリリース (基礎生物学研究所)(東京大学) |
| (21) Ishikawa T, Okada T, Ishikawa-Fjiwara T, Todo, T, Kamei Y, Shigenobu S, Tanaka M, Saito T L, Yoshimura J, Morishita S, Toyoda A, Sakaki Y, Taniguchi Y, Takeda S and Mori K. (2013). ATF6α/β-3ediated adjustment of ER chaperone levels is essential for development of the notochord in medaka fish. Mol. Biol. Cell., 24, 1387-1395. |
| (20) Ikehata H, Higashi S, Nakamura S, Daigaku Y, Furusawa Y, Kamei Y, Watanabe M, Yamamoto K, Hieda K, Munakata N and Ono T. (2013). Action spectrum analysis of UVR genotoxicity for skin: The border wavelengths between UVA and UVB can bring serious mutation loads to skin. J. Invest. Dermatol., 133 1850-1856. |
| (19) Shikata T, Matsunaga S, Iseki M, Nishide H, Higashi S, Kamei Y, Yamaguchi M, Jenkinson I R and Watanabe M. (2013). Blue light regulates the rhythm of diurnal vertical migration in the raphidophyte red-tide alga Chattonella antiqua. J. Plankton Res., 35, 542-552. |
| (18) Kobayashi K, Kamei Y, Kinoshita M, Czerny T and Tanaka M (2013). A heat-inducible CRE/LOXP gene induction system in medaka. Genesis, 51, 59-67, |
| 【2012】 |
| (17) Yasuda T, Oda S, Li Z, Kimori Y, Kamei Y, Ishikawa T, Todo T and Mitani H. (2012). Gamma-ray irradiation promotes premature meiosis of spontaneously differentiating testis-ova in the testis of p53-deficient medaka (Oryzias latipes). Cell Death Dis., 3, e395 |
| (16) Kitano T, Hayashi Y, Shiraishi E and Kamei Y. (2012). Estrogen rescues masculinization of genetically female medaka by exposure to cortisol or high temperature. Mol. Reprod. Dev., 79, 719-726. |

|
| This paper was selected as a cover art. |
| (15) Ansai S, Ochiai H, Kanie Y, Kamei Y, Gou Y, Kitano T, Yamamoto T and Kinoshita M. (2012). Targeted disruption of exogenous EGFP gene in medaka using zinc-finger nucleases. Dev. Growth Differ. , 54, 546-556 |
| (14) Masuyama H, Yamada M, Kamei Y, Fujiwara-Ishikawa T, Todo T, Nagahama Y and Matsuda M. (2012). Dmrt1 mutation causes a male-to-female sex reversal after the sex determination by Dmy in the medaka. Chromosome Res. , 20 163-176. |
| 【2011】 |
| (13) Shikata T, Iseki M, Matsunaga S, Higashi S, Kamei Y and Watanabe M. (2011). Blue and red light-induced germination of resting spores in the red-tide diatom Leptocylindrus danicus. Photochem. Photobiol., 87, 590-597. |
| 【2010】 |
| (12) Ishikawa T, Kamei Y, Otozai S, Kim J, Sato A, Kuwahara Y., Tanaka, M, Deguchi, T, Inohara H, Tsujimura T, Todo T. (2010). High-resolution melting curve analysis for rapid detection of mutations in a Medaka TILLING library. BMC Mol. Biol, 11, 70 (#;equally contribution) |
| (11) Hayashi Y, Kobira H, Yamaguchi T, Shiraishi E, Yazawa T, Hirai T, Kamei Y and Kitano T. (2010). High temperature causes masculinization of genetically female medaka by elevation of cortisol. Mol. Reprod. Dev., 77, 679-686 
|
| This paper was selected as a cover art. |
| (10) Oda S, Mikami S, Urushihara Y, Murata Y, Kamei Y, Deguchi T, Kitano T, Fujimori K E, Yuba S, Todo T and Mitani H. (2010). Identification of a functional medaka heat shock promoter and characterization of its ability to induce exogenous gene expression in medaka in vitro and in vivo. Zool. Sci., 27, 410-415 |
| (9) Deguchi T, Itoh M, Urawa H, Matsumoto T, Nakayama S, Kawasaki T, Kitano T, Oda S, Mitani H, Takahashi T, Todo T, Sato J, Okada K, Hatta K, Yuba S and Kamei Y. (2009). Infrared laser-mediated local gene induction in medaka, zebrafish and Arabidopsis thaliana. Dev. Growth Differ., 51(9), 769-775 (corresponding author) |
| (8) Kamei Y, Suzuki M, Watanabe K, Fujimori K, Kawasaki T, Deguchi T, Yoneda Y, Todo T, Takagi S, Funatsu T and Yuba S. (2009). Infrared laser-mediated gene induction in targeted single cell in vivo. Nature Methods, 6, 79-81 (2009) (*;corresponding author) |
| 【2008以前】 |
| (7) Tomida J, Masuda Y, Hiroaki H, Ishikawa T, Song I, Tsurimoto T, Tateishi S, Shiomi T, Kamei Y, Kim J, Kamiya K, Vaziri C, Ohmori H and Todo T. (2008). DNA damage-induced ubiquitylation of RFC2 subunit of replication factor C complex. J. Biol. Chem., 283, 9071-9079 |
| (6) Kamei Y, Itou J, Oda S, Masui M, Kim J H, Ishikawa T, Yuba S, Kinoshita M, Mitani H and Todo T. (2007). Development of a convenient in vitro fertilization method using interspecific hybrids between Oryzias latipes and Oryzias curvinotus. Dev. Growth Differ., 49, 721-730 |
| (5) Taniguchi Y, Takeda S. Furutani-Seiki M, Kamei Y, Todo T, Sasado T, Deguchi T, Kondoh H, Mudde J, Yamazoe M, Hidaka M, Mitani H, Toyoda A, Sakaki Y, Plasterk R H and Cuppen E. (2006). Generation of medaka gene knockout models by target-selected mutagenesis. Genome Biology, 7(12):R116 |
| (4) Kondo Y, Kondoh J, Hayashi D, Ban T, Takagi M, Kamei Y, Tsuji L, Kim J and Yoneda Y. (2002). Molecular cloning of one isotype of human lamina-associated polypeptide 1s and a topological analysis using its deletion mutants. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 294 (4), 770-778. |
| (3) Kobayashi Y, Ishikawa T, Hirayama J, Daiyasu H, Kanai S, Toh H, Fukuda I, Tsujimura T, Terada N, Kamei Y, Yuba S, Iwai S and Todo T. (2000). Molecular analysis of zebrafish photolyase/cryptochrome family: two types of cryptochromes present in zebrafish. Genes Cells, 5 (9), 725-738. |
| (2) Kamei Y, Yuba S, Nakayama T and Yoneda Y. (1999). Three distinct classes of the α-subunit of the nuclear pore-targeting complex (importin-α) are differentially expressed in adult mouse tissues. J. Histochem. Cytochem., 47 (3), 363-372. |
| (1) Imamoto N, Kamei Y and Yoneda Y. (1998). Nuclear transport factors: function, behavior and interaction. Eur. J. Histochem, 42 (1), 9-20. |