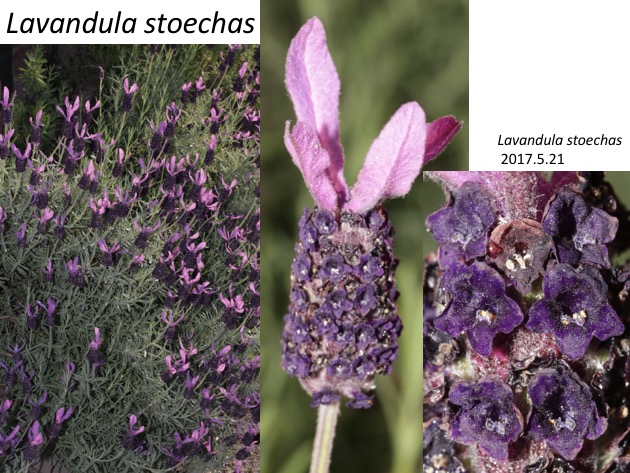

ラベンダー属は約36種がマクロネシア、地中海盆地、北アフリカ、北東アフリカ、南西アフリカ、南西アジア、アラビア半島、インド中部と南部に分布する(Harley et al. 2004)。Lavandula stoechasは地中海周辺に野生する(Upson and Andrews 2004)。
Lavandula includes approximately 36 species, which are distributed in Macronesia, Mediterranean basin, North and North East Africa, South West Africa, South West Asia, Arabian Peninsula, and Central and south India (Harley et al. 2004). Lavandula stoechas is distributed in Mediterranean regions (Upson and Andrews 2004).
Harley, R.M., Atkins, S., Budantsev, A.L., Cantino, P.D., Conn, B.J., Grayer, R., Harley, M.M., de Kok, R., Krestovskaja, T., Morales, R., Paton, A.J., Ryding, O., and Upson, T. 2004. Labiatae. In Kubitzki, K. ed. The Families and Genera of Vascular Plants VII: Kadereit, J.E. ed. Flowering Plants. Dicotyledons: Lamiales (except Acanthaceae including Avicenniaceae). Springer, Berlin.
Upson, T. and S. Andrews 2004. The Genus Lavandula, Botanical Magazine Monograph. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew.
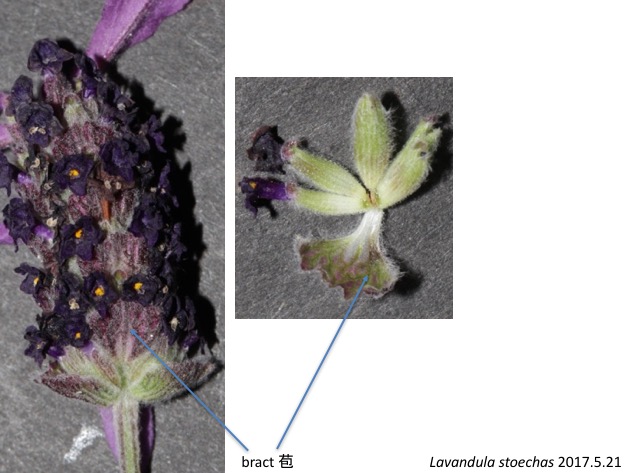

花序の中の位置によって、1つの苞に5つ(基部側)から1つ(頂端側)の花が抱かれる。
A bract subtends five flowers to one flower depending on its position in an inflorescence.
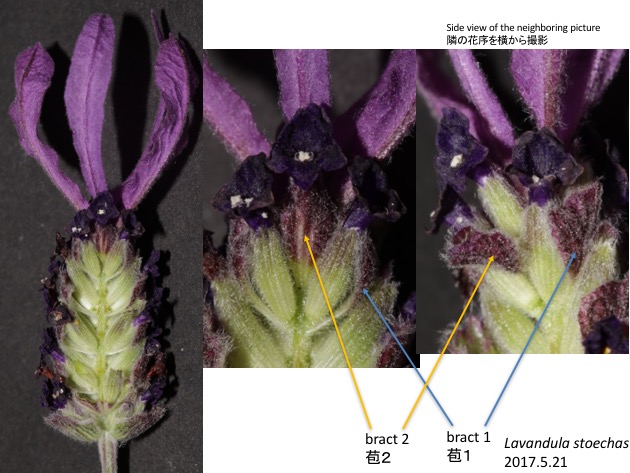

花序の先端側の4枚の苞は、他の苞より大きく綺麗になる。ガガイモ属(Wilson and Price 1977)、ベゴニア属 (Schemske and Agren 1995)、ヒエンソウ属 (Waser and Price 1991)、スミレ科のヒバツス属 (Augspurger 1980)などで訪花昆虫を誘引するコストを増やすと、媒介昆虫の数も増えているという研究結果が報告されている。しかし、Lavandula stoechasの場合は、野外集団で、花弁状苞を取り除いた個体と取り除いていない個体を比較しても、両者で訪花昆虫数、種子数に統計的に有為な違いは見られなかった(Herrera 1997)。このことから、Lavandula stoechasの花弁状苞は、訪花昆虫が十分にいる通常状態ではなく、訪花昆虫が少ない、あるいは、少数の植物体だけが生育している場合などに適応的なのかもしれない(Herrera 1997)。
Most distal four bracts are larger and more colorful than other bracts. Several reports showed the positive relationships between costs in advertisement and pollinator visitations in Asclepias (Wilson and Price 1977), Begonia (Schemske and Agren 1995), Delphinium (Waser and Price 1991), Hybanthus (Augspurger 1980), and so on (Gori 1983). However, the removal of large and colorful bracts in Lavandula stoechas did not significantly reduce pollinator visitation rates and fecundity in wild populations, implying that those bracts function in unusual conditions, including extremely low plant density (Herrera 1997).
Augspurger, C. K. 1980. Mass-flowering of a tropical shrub (Hybanthus prunifolius): influence on pollinator attraction and movement. Evolution 34:475-488.
Gori, D. F 1983. Post-pollination phenomena and adaptive floral changes. Pages 31-49 in C. E. Jones and R. J. Little, editors. Handbook of experimental pollination biology. Sci- entific and Academic Editions, New York, New York, USA.
Herrera J. 1997 The role of colored accessory bracts in the reproductive biology of Lavandula stoechas. Ecology 78, 494–504.
Stearn, W.T. 1992 Botanical Latin 4th ed. Timber Press, Oregon.
Schemske, D. W., and J. Agren. 1995. Deceit pollination and selection on female flower size in Begonia involucrata: an experimental approach. Evolution 49:207-214.
Waser, N. M., and M. V. Price. 1991. Outcrossing distance effects in Delphinium nelsonii: pollen loads, pollen tubes, and seed set. Ecology 72:171-179.
Willson, M. F, and P. W. Price. 1977. The evolution of in- florescence size in Asclepias (Asclepiadaceae). Evolution 31:495-511.
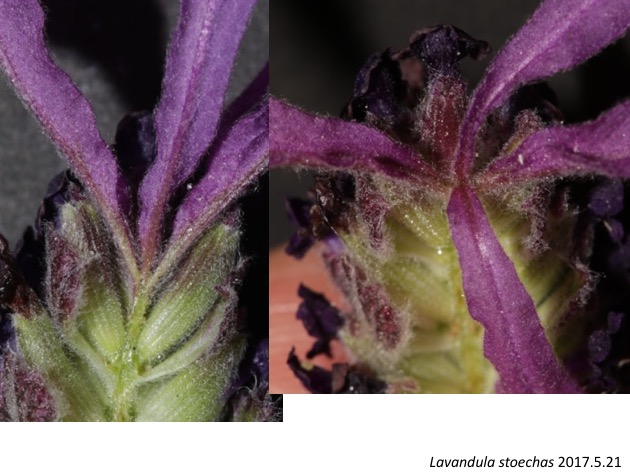

大きな苞の腋には花ができない。苞と花は同じ原基から形成されるが、原基の大きさが限定されているとすると、苞が大きくなると原基の大部分を占めてしまうため花ができないのかもしれない。逆に、花ができないからその分、苞への割当が増え、苞が大きくなったのかもしれない。
No flowers are formed at the axils of large bracts. If the size of a primordium to form a bract and flower (s) is limited, a primordium can make only a bract and no flowers when a bract becomes larger. On the other hand, a lack of flower initiation might result in the extra space for a large bract.
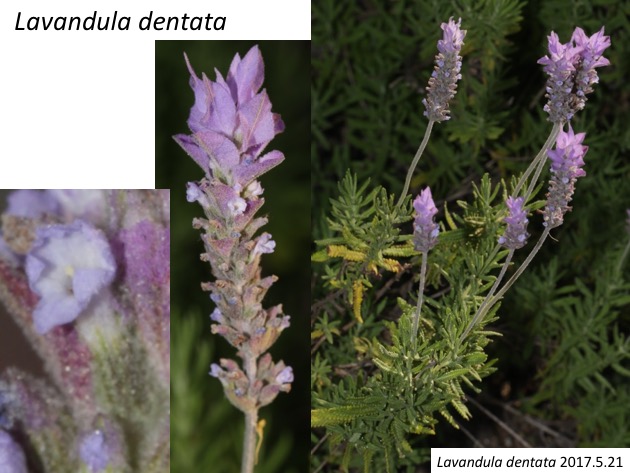

Lavandula dentataは、地中海地域に分布する (Upson and Andrews 2004)。先端の約10枚の苞が大きく、カラフルになる。
Lavandula dentata is distributed in the Mediterranean region (Upson and Andrews 2004). Lavandula dentata forms approximately ten large bracts in comparison to usually four in Lavandula stoechas.
Upson, T. and S. Andrews 2004. The Genus Lavandula, Botanical Magazine Monograph. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew.
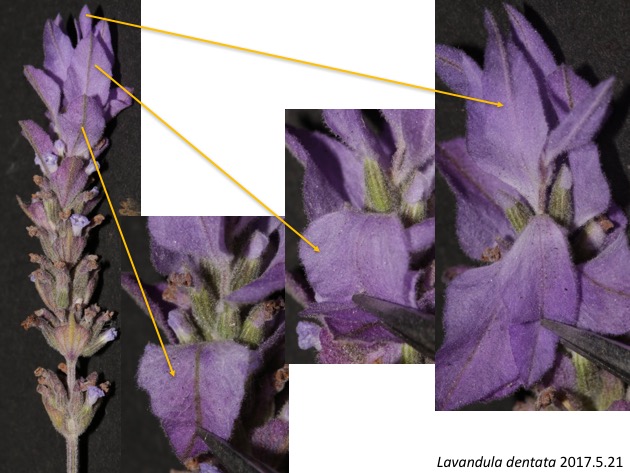

花序の基部側の苞は約3個の花を抱き、中央付近の苞は1個、先端近くの苞は花を抱かない。Lavandula stoechas と Lavandula dentata の違いはどのような発生の仕方の違いによって生じているのだろうか。
More basal large bracts subtend approximately three flowers, middle ones one flower, and distal three or four bracts do not any flowers. What is the developmental difference between Lavandula stoechas and Lavandula dentata?

Salvia virdisでは、花序先端部分の苞が花を着ける苞より大きくなって紫に色づくが、苞の腋には花がつかない。これら以外の苞は、緑色で腋に花を付ける。このような違いはどのように発生過程を変えることによって引き起こされているのだろうか。進化の過程で全く新しいものを作り出すことはほとんどなく、体のどこか別の場所で使ってた発生機構、遺伝子系を用いている場合が多い。色の付いている花弁の遺伝子系を流用したのだろうか。では、紫色の苞が緑の苞よりも大きくなる点はどうだろう。どうやって特定の器官を大きくするのだろうか。
Large and colorful bracts are also observed in Salvia and do not subtend flowers. Basal bracts are greenish and how these large and colorful bracts acquired the developmental system during the evolution. At least,
Genetic regulatory network for color pigmentation appears to be coopted from that used in petals, while it is difficult to hypothesize the evolution of the additional growth.
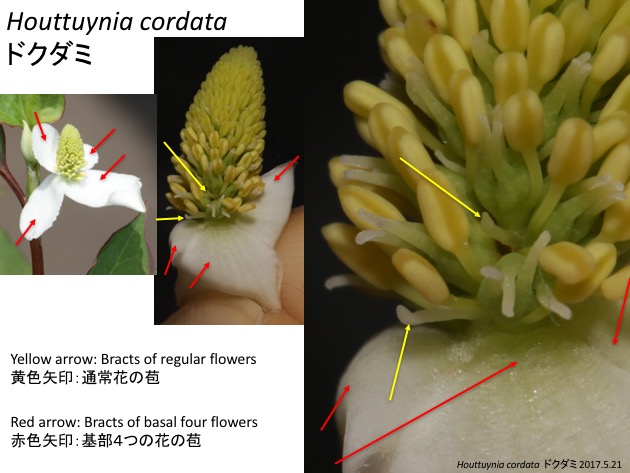
ドクダミの花序は、基部の4つの花の苞(赤矢印)が他の花の苞(黄色矢印)よりも大きくなり、花序全体で一つの花のように見える偽花となっている。シソ科のラベンダー属やサルビア属のように苞の大きさが変化しているが、器官の大きさを制御する仕組み、いろいろな植物で同じ仕組みを使っているのかはまだよくわかっていない。
In the pseudanthium of Houttuynia cordata in the Piperaceae, basal four flowers are subtended by large and white bracts, while other flowers are by tiny and white bracts. This suggests that bracts of basal four flowers evolved to become larger, or bracts except basal four to become smaller. Again, molecular and developmental mechanisms to regulate the organ size is not well understood and we do not know what change of genetic regulatory networks caused such evolution.
