
National Institute for Basic Biology





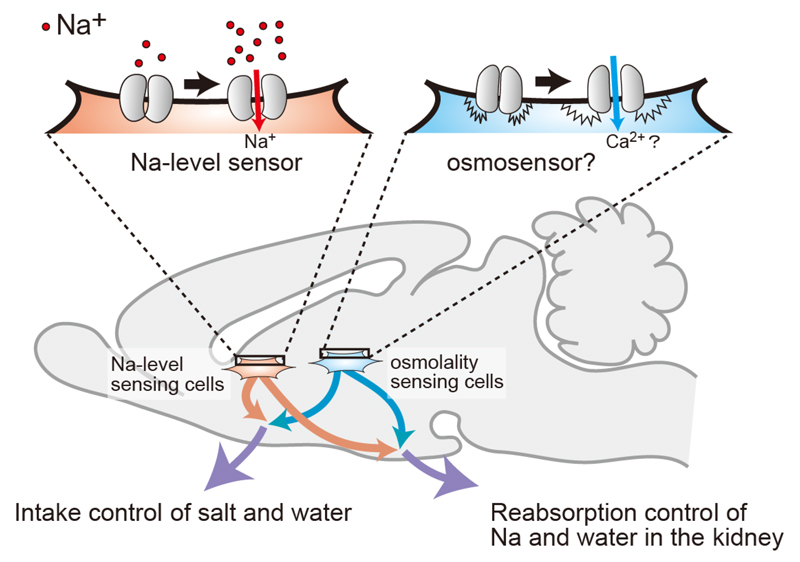
Visual overview: Two postulated systems for sensing body-fluid conditions
The homeostatic osmoregulation of body fluids (such as plasma and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)) is vital to life. This is because substantial changes in cell volumes due to hypertonicity or hypotonicity cause irreversible damage to organs and lead to lethal neurological trauma. Water deprivation (loss of water from the body) elevates the concentration of Na+ ([Na+]) and osmolality in body fluids. Animals exhibit prominent and effective responses to water deprivation, including behavioral responses, such as inducing water intake and avoiding sodium (Na), along with vasopressin-induced reductions in urine volumes. The aim of our research group is to reveal the brain systems for body-fluid homeostasis.
[Na+] is the main factor influencing osmolality in vivo, and is continuously monitored in the brain to be maintained within a physiological range. We have shown that Nax, which structurally resembles voltage-gated sodium channels (Nav1.1–1.9), is the brain [Na+] sensor to detect increases in [Na+] in body fluids. Nax is preferentially expressed in specific glial cells of sensory circumventricular organs (sCVOs) including the subfornical organ (SFO) and organum vasculosum lamina terminalis (OVLT). We have found that Nax signals in these brain regions deficient in a blood-brain barrier are involved in the control of salt intake.
We demonstrated that Nax signals are also involved in the control of water intake behavior. The signaling mechanisms in the OVLT for water-intake induction by increases in [Na+] in body fluids are presented in Figure 1. When [Na+] in plasma and CSF increases, Nax channels in glial cells in the OVLT are activated, leading to the synthesis of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs) in Nax-positive glial cells. EETs released from Nax-positive glial cells function as gliotransmitters to activate neurons bearing TRPV4 channels in the OVLT, which are involved in the stimulation of water-intake behavior.
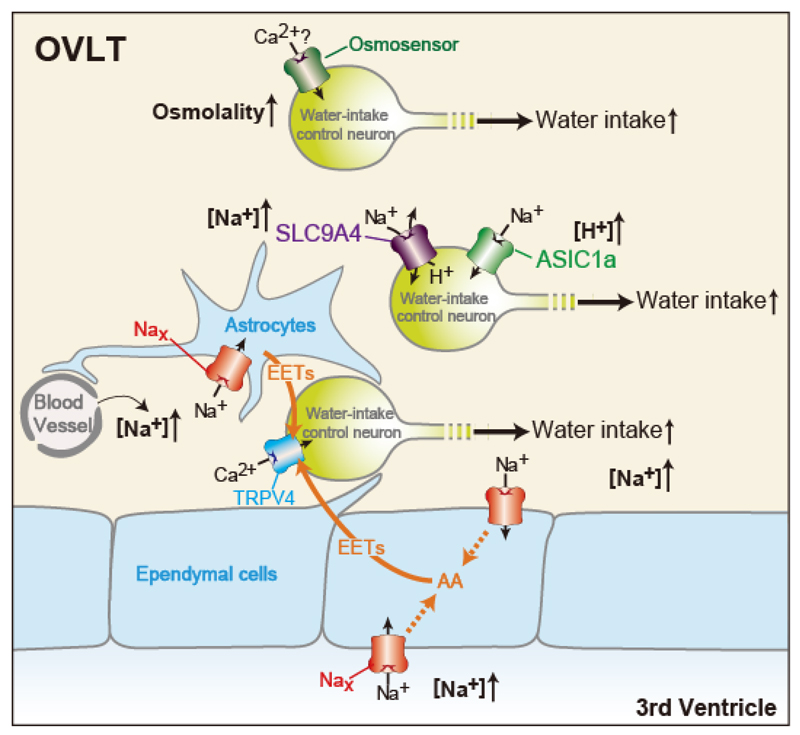
Figure 1. Schematic drawings of sensing mechanisms of body-fluid conditions in the OVLT responsible for the induction of water intake. AA, arachidonic acid.
Water intake by Nax-KO mice after an ICV injection of hypertonic NaCl solution was small, but still approximately half that of WT mice. It was noteworthy that this was significantly higher than that of Nax-KO and WT mice after an ICV injection of an equimolar hypertonic sorbitol solution. These findings suggest the existence of another unknown [Na+] sensor and osmosensor. In order to identify the novel sensors involved in water intake control, we performed RNA-seq analysis of OVLT and identified many candidates for said sensors. As a result, we revealed that SLC9A4 in the OVLT functions as a [Na+] sensor for the control of water intake behavior among these candidates, and that the signaling pathway originating from this sensor is independent of the Nax/TRPV4 pathway, another [Na+]-sensing pathway for the control of water intake (Figure 1). Our experimental results suggested that SLC9A4-positive neurons are activated via ASIC1a in a H+-dependent manner. Our experimental results also revealed that water intake induced by the increase in [Na+] in CSF was completely lost in slc9a4-knockdown Nax-KO mice. Thus, water intake induced by [Na+] increases in body fluids may be explained by the Nax/TRPV4 and SLC9A4/ASIC1a pathways. In addition to these two [Na+]-dependent pathways that induce water intake, another signaling pathway originating from the osmosensor may be independently involved in the induction of water intake. We are now examining the functional roles of remaining candidates in water intake to clarify the osmosensing system.