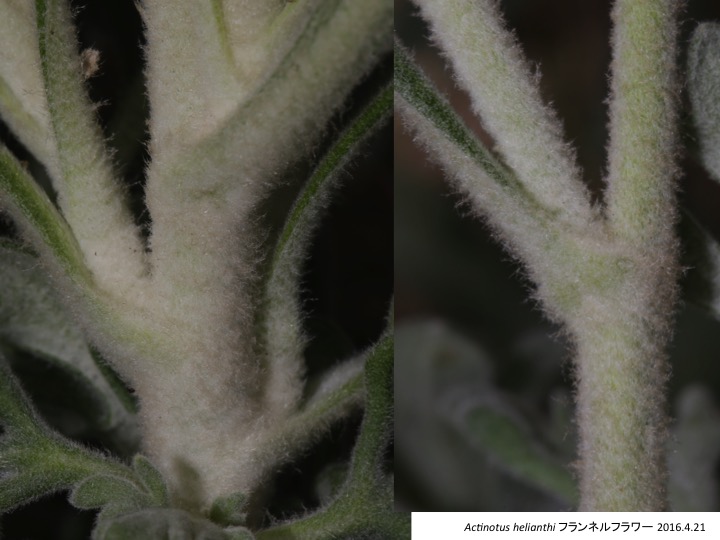
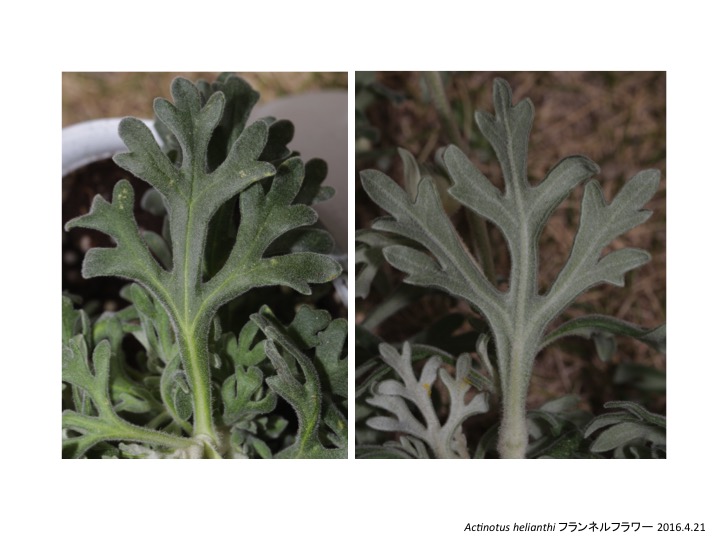
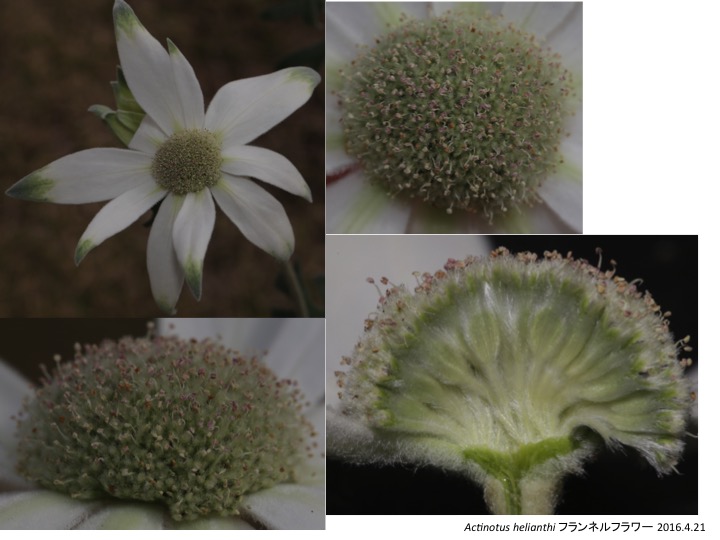
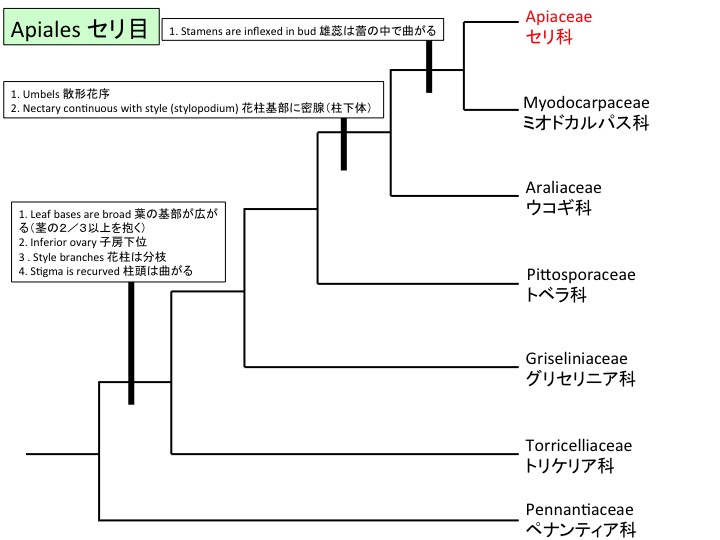
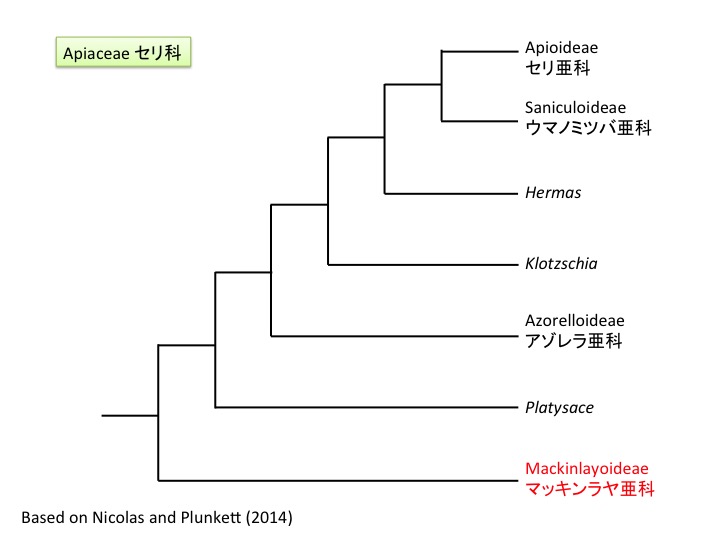
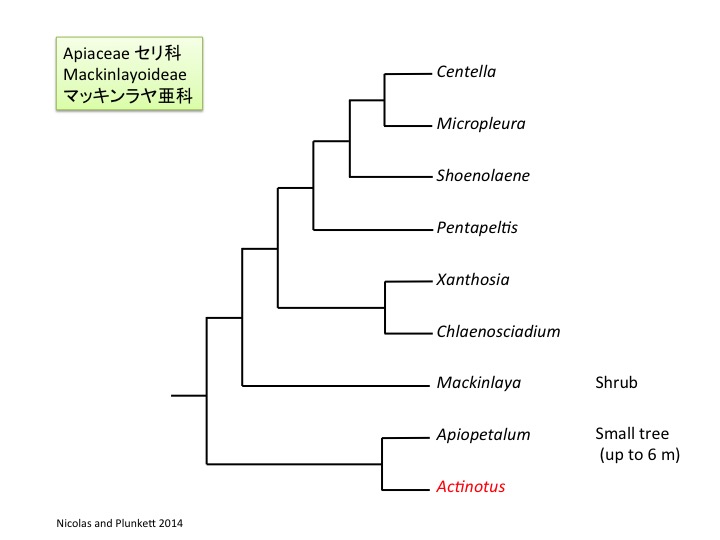
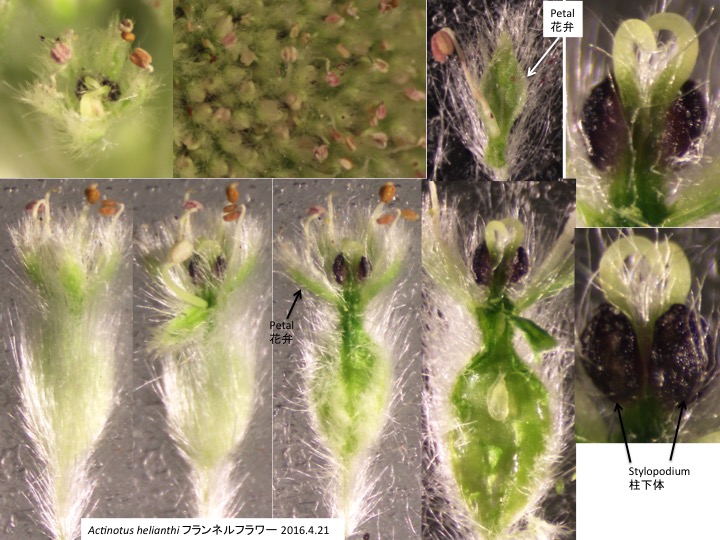
Actinotus フランネルフラワー属は19種がオーストラリアとニュージーランドに分布する(Henwood 2013)。
Actinotus is distributed in Australia and New Zealand (Henwood 2013).
Henwood, M.J. 2013. Actinotus repens Keighery ex Henwood (Apiaceae): A new species from south-west Western Australia. TELOPEA 15: 221-225.
柱下体は花筒に包まれずむき出しになっている。
Stylopodiua are not covered by hypanthium.
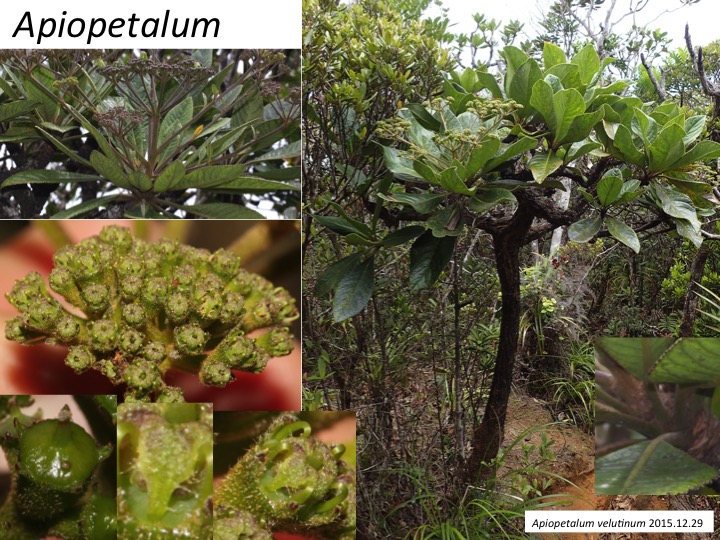
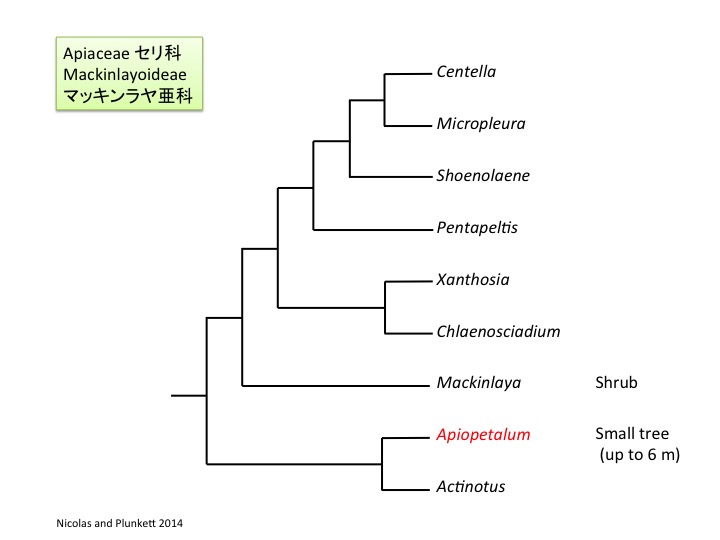
Apiopetalum属は2種からなりニューカレドニアの固有種で、大きくなると約6mほどの木になり(Oskolski and Lowry 2000)、セリ科よりもウコギ科に似ている。しかし、セリ科の共有派生形質である、かぎ爪状の花弁、2心皮性雌蕊、葉柄基部が茎全体を取り巻くという形質を持っており(Oskolski and Lowry 2000)、遺伝子配列比較からもセリ科であると推定されている (Nicolas and Plunkett 2014)。
Apiopetalum is composed of two species endemic in New Caledonia (Oskolski and Lowry 2000). Instead of the woody nature unusual in the Apiaceae and usual in the Araliaceae, some characters including the presence of clawed petals, a bicarpellate gynoecium, and leaf bases encircling a stem are shared with other species in the Apiaceae (Oskolski and Lowry 2000). Inclusion of Apiopetalum in the Apiaceae is supported by molecular phylogenetic analyses (Nicolas and Plunkett 2014).
Nicolas, A. N. and Plunkett, G. M. 2014. Diversification times and biogeographic patterns in Apiales. Bot. Review 80: 30-58.
Oskolski, A.A. and Lowry II, P.P. 2000. Wood Anatomy of Mackinlaya and Apiopetalum (Araliaceae) and Its Systematic Implications. Ann. Missouri Bot. Gard. 87: 171-182.
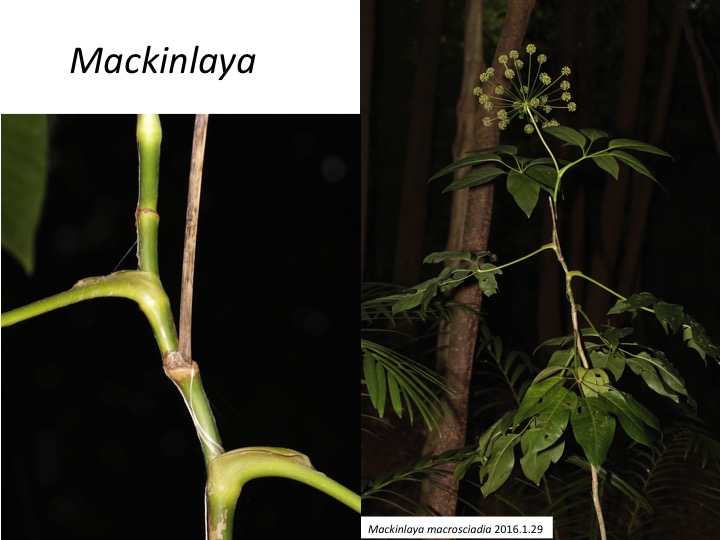
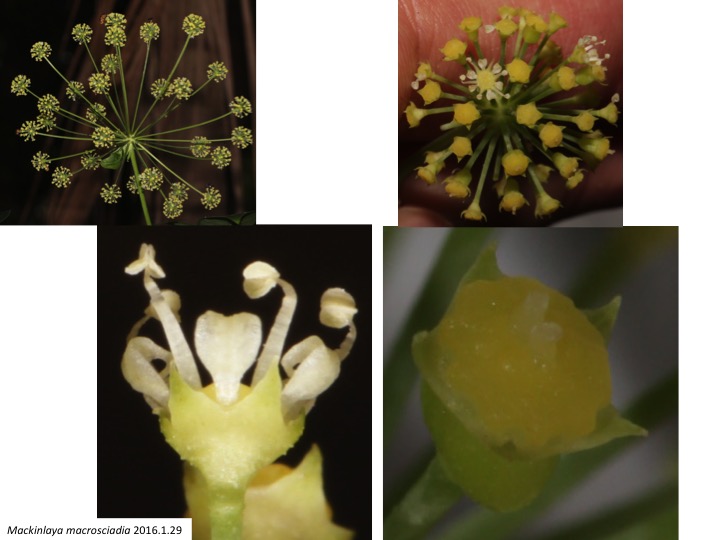
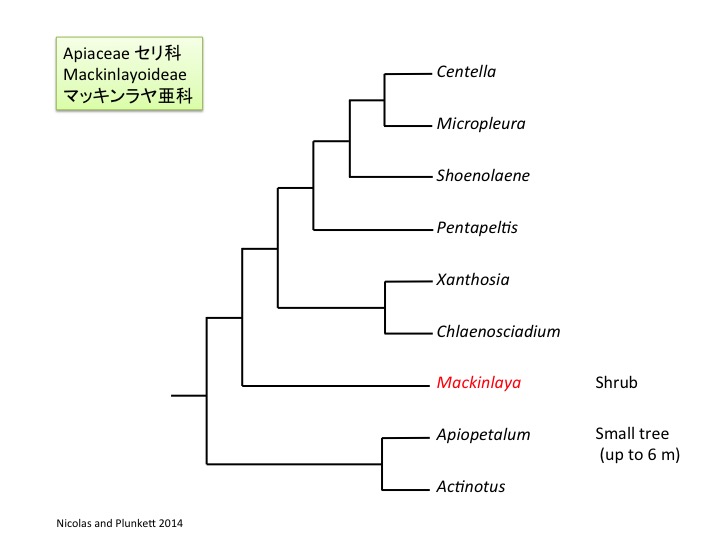
マッキンラヤ属は5種からなり(Philipson 1979)、オーストラリアからマレーシアに分布している(Nicolas and Plunkett 2014)。低木になる点はセリ科では木になるApiopetalumのように稀である。しかし、葉柄基部が茎を抱く点はセリ科の共有派生形質である。
Mackinlaya is composed of five species (Philipson 1979) and distribute from Australia to Malesia (Nicolas and Plunkett 2014). Although the shrubby morphology is unusual in the Apiaceae as the woody Apiopetalum, “leaf bases encircling a stem“ is a synapomorphic character of the Apiaceae.
Nicolas, A. N. and Plunkett, G. M. 2014. Diversification times and biogeographic patterns in Apiales. Bot. Review 80: 30-58.
Philipson, W.R. 1979. Araliaceae, part 1. Ed. C.G.G.J. van Steenis, Flora Malesiana, Ser. I, 9: 1-105. Martinus Nijhoff, Dr. W. Junk Publishers, The Hague, Boston, London.
さらに、舷部のある花弁、心皮性の子房、そして、分子系統解析の結果もセリ科の一員であることを示している。
In addition, clawed petals, a bicarpellate gynoecium, and molecular phylogeny inference support its inclusion in the Apiaceae.
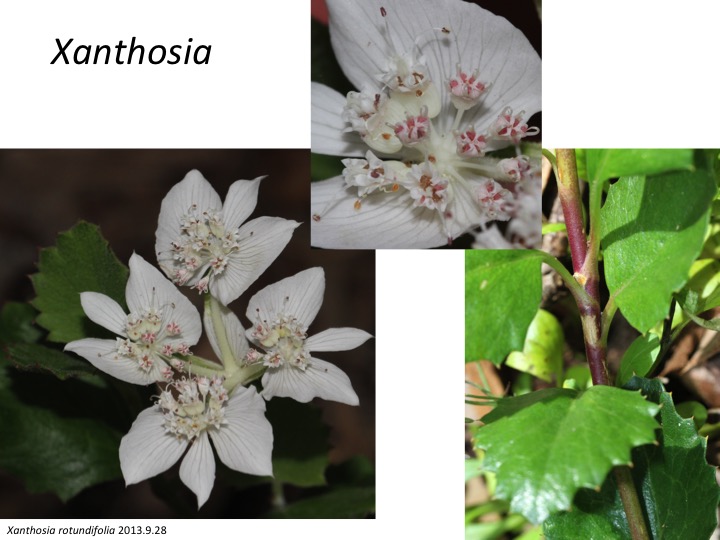
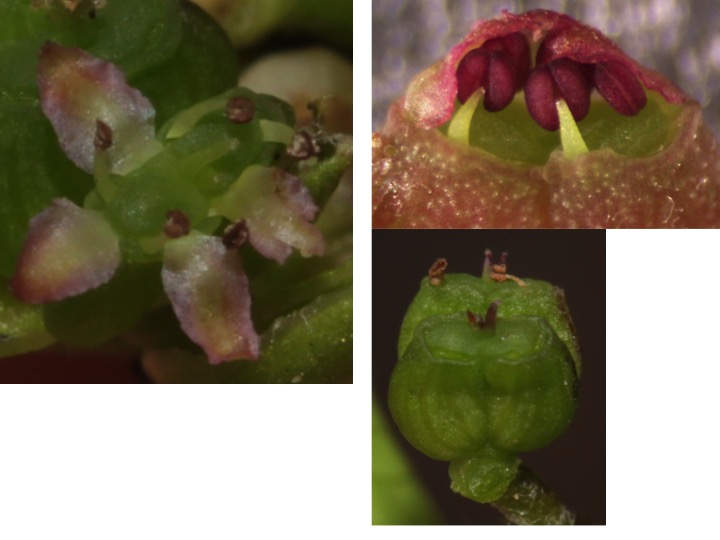
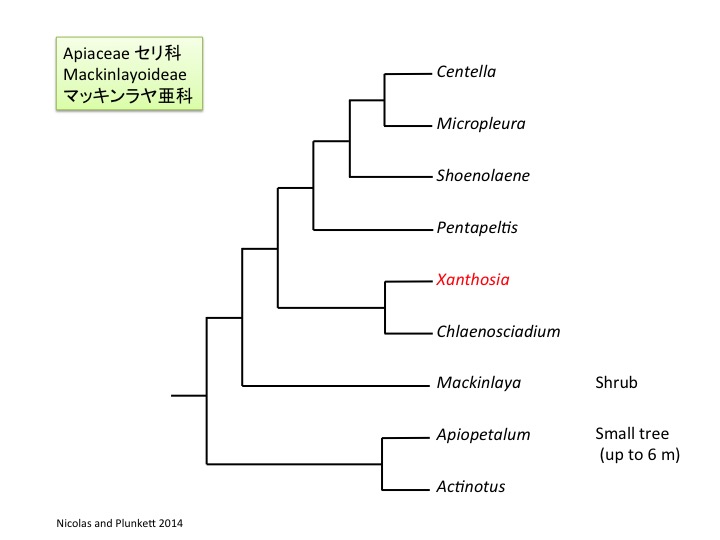
Xanthosia属は約20種からなり、オーストラリアに分布している。Xanthosia rotundifoliaの総苞は花弁化している。
Xanthosia is composed of about 20 species and is distributed in Australia. Xanthosia rotundifolia forms petaloid bracts.
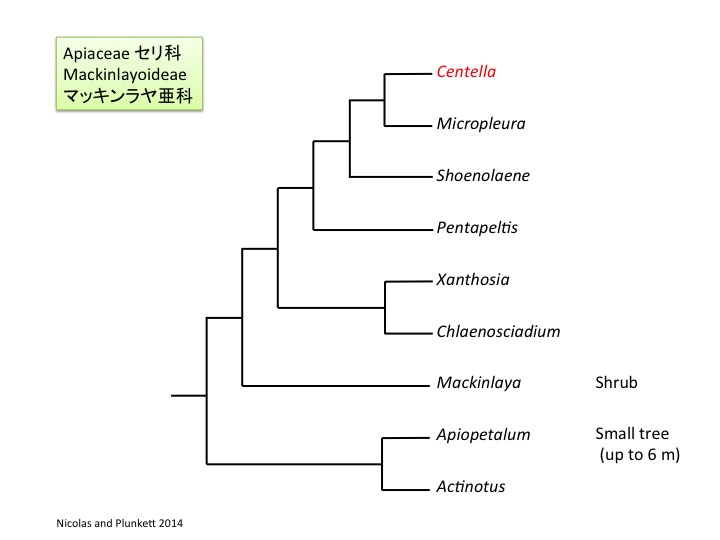
ツボクサ属は約100種が世界中に分布する。
茎が這って節から根を出すことや腋生の花序がチドメグサ属 Hydrocotyleとツボクサ属 Centellaで似ているが、遺伝子解析から、チドメグサ属はウコギ科、ツボクサ属はセリ科に属することがわかった。
ツボクサ属はセリ科の以下の2つの共有派生形質を共有している:1つは葉柄基部が茎を取り巻くことである。
Although the creeping stem, axillary inflorescences, and adventitious roots from nodes are similar between Hydrocotyle and Centrella, Hydrocotyle belongs in the Araliaceae and Centella in the Apiaceae.
Centella share the following two synapomorphic characters of the Apiaceae: (1) Leaf bases encircle a stem.
もう一つは花弁辺縁が内側に曲がり、かぎ爪状であることである。しかし、セリ科に広く見られる子房の油管は無い。
「蕾の中で著しく曲がる雄しべ」はセリ科とミオドカルパス科の共有派生形質であるが、ツボクサ属の雄しべは蕾の中でそれほど曲がらない。
(2) Petals are clawed at the base and inflexed at the tips. On the other hand, Centella do not have oil canals in the fruits, although it is synapomorphic character of the Apiaceae.
“Extensively inflexed stamens in a flower bud” is a synapomorphic character of the Apiaceae and Myodocarpaceae, but stamens of Centella are not so inflexed.