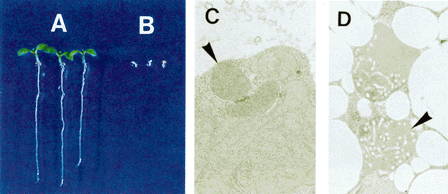
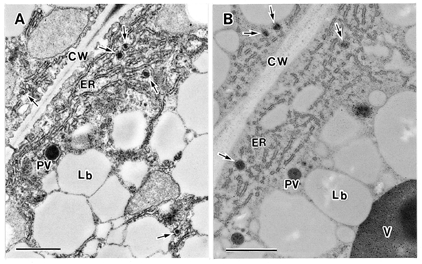
NATIONAL INSITUTE FOR BASIC BIOLOGY

National Institute for Basic Biology
DIVISION OF CELL MECHANISMS
- Professor:
- Mikio Nishimura
- Associate Professor:
- Ikuko Hara-Nishimura
- Research Associates:
- Makoto Hayashi
- Tomoo Shimada
- Post doctoral fellows:
- Tetsu Kinoshita
- Akira Kato (~ Aug. 30 )
- Nagako Hiraiwa (~ March 30 )
- Yasuko Ishimaru
- Kanae Shirahama
- Shoji Mano
- Akira Kato (~ Aug. 30 )
- Graduate Students:
- Hiroshi Hayashi
- Kenji Yamada
- Naoto Mitsuhashi
- Kazumasa Nito
- Yuki Tachibe (from Hiroshima University)
- Kenji Yamada
- Technical Staffs:
- Maki Kondo
- Katsushi Yamaguchi
- JSPS Technical Staffs:
- Miwa Kuroyanagi
- Kanako Toriyama (~ Nov. 30 )
- Miki Kinoshita (April .1 ~ )
- Chizuru Ueda (April .1 ~ )
- Chihiro Nakamori (April .1 ~ )
- Kanako Toriyama (~ Nov. 30 )
- Visiting Scientists:
- Roland R. Theimer (Bergische Univ. Germany )
- Yasuko Koumoto