|
 |
 |
| |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
核膜孔複合体のダイナミクス:メカニズムと制御
平成17−18年度
核膜サブドメインを形成する分子機構と形成機構の解析
平成19−20年度 |
 |
| 理研基幹研 今本細胞核機能研究室 今本尚子 |
| |
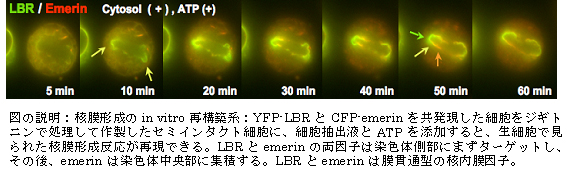
真核生物が進化の過程で獲得した核膜は、遺伝子を封入して遺伝子機能を担う因子群を濃縮するだけでなく、高次クロマチン構築の足場として遺伝子機能を支える細胞内構造である。核膜とクロマチンの物理的・機能的繋がりを探るため、研究期間前半(H17-H18)では核膜に存在する最も顕著な構造体である核膜孔複合体に注目し、その挙動を調べた。その結果、核膜孔複合体の分布が細胞分裂終期に核膜が形成されるときに定まること、また、その分布がG1初期の細胞運命が決定される時期に崩れること、更に、核膜孔複合体の分布にlaminなどの核内膜因子が積極的に寄与するとがわかった。細胞機能に即して規則的に変化する核膜上の領域を核膜サブドメインと名付けた(業績15)。研究期間後半(H19-H20)では核膜サブドメインが形成される分子過程をヒト細胞で解析するための実験系の樹立に力を注いだ。ライブ観察から、核膜形成初期に核内膜や核膜孔複合体などの因子群が染色体の特定部位にまず集積し、その後局在化することでサブドメインが形成されることを確認した。この過程の生化学的解析には、分裂期のセミインタクト細胞の利用(業績6)が有用であることに気付いた。核膜孔複合体因子や異なるサブドメインに局在する核内膜因子の各々に、異なる蛍光タンパク質を結合して同時に2種タンパク質を安定に発現する細胞株を取得した(関連業績9, 10, 11)。そのセミインタクト細胞に細胞抽出液を添加すると、核膜因子が染色体上へターゲットし、更に、局在化した。生細胞で見られる核膜形成初期反応を、in vitroで再構築できるのである(下図)。この系を利用することにより、核膜形成を担う可溶性因子や核膜因子の局在化機構、並びに、核膜因子を集積させる染色体側要素の解析が可能になる。
|
| |
発表論文リスト:
- Watanabe N, Sekine T, Takagi M, Iwasaki JI, Imamoto N, Kawasaki H, Osada H. Deficiency in chromosome congression by the inhibition of PLK1 polo box domain-dependent recognition. J. Biol. Cellin press.
- Nishino, Y., Takahashi, Y., Imamoto, N., Ishikawa, T., and Maeshima, K. Three-Dimensional Visualization of a Human Chromosome Using Coherent X-ray Diffraction. Phy. Rev. Lett. in press.
- Takagi, M., Bunai, K., Yanagi, K., and Imamoto, N. (2008). Cloning of Xenopus orthologs of Ctf7/Eco1 acetyltransferase and initial characterization of XEco2. FEBS J., 275, 6109-6122.
- Kuriyama I, Mizuno T, Fukudome K, Kuramochi K, Tsubaki K, Usui T, Imamoto N, Sakaguchi K, Sugawara F, Yoshida H, Mizushina Y. (2008). Effect of dehydroaltenusin-C12 derivative, a selective DNA polymerase alpha inhibitor, on DNA replication in cultured cells. Molecules. 13, 2948-2961
- Hatakeyama M., Tomizawa, T., Sakai-Kato, K., Bouvagnet, P., Kose, S., Imamoto, N., Yokoyama, S., Itsunomita-Tate, N., Mikoshiba, K., Kigawa, T., Aruga, J. (2008). Functional and structural basis of the nuclear localization signal in the ZIC3 zinc finger domain. Hum. Mol. Genet. in press
- Tahara, K,, Takagi, M., Ohsugi, M., Sone,T., Maeshima, K., Horiuchi,Y., Tokai-Nishizumi, N., Fumiko Nishiumi, F., Imamoto, F., Yamamoto, T., Kose, S. and Imamoto, N. (2008). Importin β and small GTPase Ran mediates the chromosome loading of human chromokinesin KID. J. Cell Biol., 180, 493-506.
- Tokunaga, M., Imamoto N., and Sakata-Sogawa, K. (2008). Highly inclined thin illumination enables clear single-molecule imaging in cells. Nature Methods. 5, 159-161. 7.
- Iwai, Y., Maeshima, K., Ikeda, T., Kojima, T.-M., Kobayashi, T.,Nebiki, T., Narusawa, T., Pokhil., G.-P., Imamoto, N., and Yamazaki, Y (2008). Ion irradiation in liquid of μm3 region for cell surgery. Applied Physics Letters 92, 023509-1-023509-3.
- Wendt, K.S., Yoshida, K., Itoh, T., Bando, M., Koch, B., Schirghuber, E., Tsutsumi, S., Nagae, G., Ishihara, Ko., Mishiro, T., Yahata, K., Imamoto, F., Aburatani, H., Nakao, M., Imamoto, N., Maeshima, K., Shirahige, K., and Peters, J.-M. (2008). Cohesin is required for the transcriptional insulator function of CTCF binding sites. Nature, 451, 796-801.
- Yahata, K., Maeshima, K., Sone, T., Ando, T., Okabe, M., Imamoto, N., and Imamoto, F. (2007). cHS4 insulator-mediated alleviation of promoter interference during cell based expression of tandemly associated transgense. J. Mol. Biol. 374, 580-590.
- Funakoshi, T., Maeshima, K., Yahata, K., Imamoto, F., Sugano, S., and Imamoto, N.(2007). Two distinct human POM121 genes: requirement for the formation of nuclear pore complexes. FEBS Lett., 581, 4910-4916.
- Imasaki, T., Shimizu, T., Hashimoto, H., Hidaka, Y., Kose, S., Imamoto, N., Yamada, M., and Sato, M. (2007). Structural basis for substrate recognition and dissociation by human transportin 1. Mol. Cell, 28, 57-67.
- Mizushina, Y., Takeuchi, T., Takakusaki, Y., Yonezawa, Y., Mizuno., T., Yanagi, KI., Imamoto, N., Sugawara, F., Sakaguchi, K., Yoshida, H., and Fujita, M. (2007). Coenzyme Q(10) as a potent compound that inhibits Cdt1-geminin interaction. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1780, 203-213.
- Tanaka, K., Ogawa, K., Takagi, M., Imamoto, N., Matsumoto, K. and Tsujimoto, M. (2006). Rap55, a cytoplasmic mRNP component, represses translation in Xenopus Oocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 40096-40106.
- Maeshima, K., Yahata,K., Sasaki,Y., Nakatomi,R., Tachibana, T., Hashikawa,T., Imamoto,, F., and Imamoto, N. (2006). Cell cycle-dependent dynamics of nuclear pores: pore-free islands and lamins. J. Cell Sci. 119, 4442-4451.
- Handa, N., Kukimoto-Niino, M., Akasaka, R., Kishishita, S., Murayama, K., Terada, T., Inoue, M,. Kigawa, T., Kose, S., Imamoto, N., Tanaka, A., Hayashizaki, Y., Shirouzu, M., and Yokoyama, S. (2006).The crystal structure of mouse Nup35 reveals atypical RNP motifs and novel homodimerization of the RRM domain. J. Mol. Biol. 363, 114-124.
- Aratani, S., Oishi, T., Fujita, H., Nikazawa, M., Fujii, R., Imamoto, N., Yoneda, Y., Fukamizu, A., and Nakajima, T. (2006). The nuclear import of RNA helicase A is mediated by importin-α3. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 340, 125-133.
- Kose, S., Furuta, M., Koike, M., Yoneda,Y. and Imamoto, N. (2005). The 70-kD heat shock cognateprotein (hsc70) facilitates the nuclear export of the import receptors. J. Cell Biol. 171, 19-25.
- Okada, Y., Suzuki, T., Sunden, Y., Ohba,Y., Kose, S., Imamoto, N., Takahashi, H., Tanaka, S., Hall, W.W., Nagashima, K., and Sawa, H. (2005). Dissociation of heterochromatin protein 1 from lamin B receptor induced by human polyomavirus agnoprotein: role nuclear egress of viral particles. EMBO Rep. 6, 452-457.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Copyright (c) 2004-2009, nuclear-dynamics. All Rights Reserved. |
|
|
|
|