|
 |
 |
| |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| 核膜孔複合体の分子動態と核―細胞質間タンパク質輸送制御 |
 |
| 大阪大学大学院生命機能研究科 米田悦啓 平成16年度−20年度 |
| |
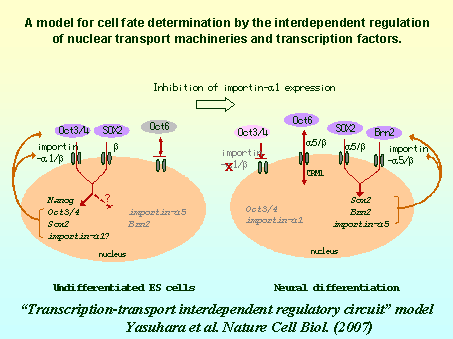
本研究課題では、細胞核の重要な高次構造の1つである核膜孔複合体に焦点を当て、この複合体の重要な機能である核―細胞質間タンパク質輸送の制御を指標にして、その分子構築ならびに分子動態を明らかにすることを目的として研究を進めてきた。核輸送のダイナミックな動態を解析するための実験系として、主として細胞分化の観点からの研究を進めた。具体的には,筋芽細胞であるC2C12細胞や未分化ES細胞を用い、細胞を未分化状態で増殖を続けさせた場合と分化誘導させた場合とで比較した場合、核膜孔複合体や核輸送因子がどのように変化するか、また、変化するのであれば、その動態を個々のヌクレオポリンや輸送因子に着目して解析するとともに、発現量、局在の変化が細胞分化にどのような影響を及ぼすかを調べた。その結果、未分化ES細胞をレチノイン酸などの処理で神経細胞へと分化誘導した場合、importin αのサブタイプの発現パターンが変化することを発見し、さらには、その発現パターンを人為的に操作するだけで、転写因子の発現パターンが変化し、未分化ES細胞を神経細胞へと分化誘導できることを見出した。これらの結果から、新しいモデルである”Transcription-transport interdependent regulatory circuit model”を提唱することができた(下図参照)。また、C2C12細胞を筋細胞に分化させた場合、核膜孔複合体全体の形態変化が起こるとともに、ヌクレオポリンの1つであるNup358の発現量が増加し、その局在が、核全体から核膜孔部分に大きく変化することを見出した。この時、同時に、蛋白質の核外輸送に関わる因子であるCRM1も核膜孔に強く局在することがわかった。さらに、siRNAを用いたNup358のノックダウン実験より、Nup358は筋細胞分化に必須の役割を果たすことを発見するとともに、CRM1による核外輸送がその分化過程で重要な役割を果たすことを示唆する成果が得られた。以上のように、本研究を通して、核輸送因子ならびに核膜孔複合体による核―細胞質間タンパク質輸送の制御が、細胞分化や細胞の運命決定に密接に関わっているという、新しい概念を提唱することができた。
|
| |
表論文リスト:
- Yamada, M., Mattaj, I. and Yoneda, Y.An ATP-dependent activity that releases RanGDP from NTF2.J. Biol. Chem., 279: 36228-36234 (2004)
- Miki, T. and Yoneda, Y.Alternative splicing of Staufen2 creates the nuclear export signal for CRM1 (exportin 1).J. Biol. Chem., 279: 47473-47479 (2004)
- Sasaki, M., Takeda, E., Takano, K., Yomogida, K., Katahira, J. and Yoneda, Y.Molecular cloning and functional characterization of mouse NXF family gene products.Genomics, 85: 641-653 (2005)
- Kotera, I., Sekimoto, T., Miyamoto, Y., Saiwaki, T., Nagoshi, E., Sakagami, H., Kondo, H. and Yoneda, Y.Importin a transports Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type IV (CaMKIV) to the nucleus without utilizing importin β.EMBO J., 24: 942-951 (2005)
- Saiwaki, T., Kotera, I., Sasaki, M., Takagi, M. and Yoneda, Y.In vivo dynamics and kinetics of pKi-67: transition from a mobile to an immobile form at the onset of anaphase.Exp. Cell Res.,308: 123-134 (2005)
- Asally, M. and Yoneda, Y. β-Catenin can act as a nuclear import receptor for its partner transcription factor, lef-1.Exp. Cell Res., 308: 357-363 (2005)
- Kose, S., Furuta, M., Koike, M., Yoneda, Y. and Imamoto, N.The 70 kDa heat shock cognate protein (hsc70) facilitates the nuclear export of the import receptors.J. Cell Biol., 171: 19-25 (2005)
- Yasuda, Y., Miyamoto, Y., Saiwaki, T. and Yoneda, Y.Mechanism of the stress-induced collapse of the Ran distribution.Exp. Cell Res., 312: 512-520 (2006)
- Kurisaki, A., Kurisaki, K., Kowanetz, M., Sugino, H., Yoneda, Y., Heldin, C.-H., and Moustakas, A.The mechanism of nuclear export of Smad3 involves exportin 4 and Ran.Mol. Cell. Biol., 26: 1318-1332 (2006)
- Shibata, S., Sasaki, M., Miki, T., Shimamoto, A., Furuichi, Y., Katahira, J., and Yoneda, Y.Exportin-5 orthologues are functionally divergent among species.Nucl. Acids Res., 34: 4711-4721 (2006)
- Nakamura, T., Arai, Y., Umehara, H., Masuhara, M., Kimura, T., Taniguchi, H., Sekimoto, T., Ikawa, M., Yoneda, Y., Okabe, M., Tanaka, S., Shiota, K. and Nakano, T.PGC7/Stella as a protector against DNA demethylation in early embryogenesis.Nature Cell Biol., 9: 64-71 (2007)
- Yasuhara, N., Shibazaki, N., Tanaka, S., Nagai, M., Kamikawa, Y., Oe, S., Kamachi, Y., Kondoh, H. and Yoneda, Y.Triggering neural differentiation of ES cells by subtype switching of importin-α.Nature Cell Biol., 9: 72-79 (2007)
- Takano, K., Miki, T., Katahira, J. and Yoneda, Y.NXF2 is involved in cytoplasmic mRNA dynamics through interactions with motor proteins.Nucl. Acids Res., 35: 2513-2521 (2007)
- Bradatsch, B., Katahira, J., Kowalinski, E., Bange, G., Yao, W., Sekimoto, T., Baumgartel, V., Boese, G., Bassler, J., Wild, K., Peters, R., Yoneda, Y., Sinning, I. and Hurt, E.Arx1 functions as an unorthodox nuclear export receptor for the 60S pre-ribosomal subunit.Mol. Cell, 27: 767-779 (2007)
- Yasuhara, N. and Yoneda, Y.Normal brain development in importin-α5 deficient-mice. Nature Cell Biol., 9: 1339 (2007)
- Katahira, J., Miki, T., Takano, K., Maruhashi, M., Uchikawa, M., Tachibana, T. and Yoneda, Y.Nuclear RNA export factor 7 is localized in processing bodies and neuronal mRNA granules through interactions with shuttling hnRNPs.Nucl. Acids Res., 36: 616-628 (2008)
- Yudin, D., Hanz, S., Yoo, S., Iavnilovitch, E., Willis, D., Gradus, T., Segal-Ruder, Y., Ben-Yaakov, K., Hieda, M., Yoneda, Y., Twiss, J. L. and Fainzilber, M.Localized regulation of axonal RanGTPase controls retrograde injury signaling in peripheral nerve.Neuron, 59: 241-252 (2008)
- Otsuka, S., Iwasaka, S., Yoneda, Y., Takeyasu, K. and Yoshimura, S. H.Individual binding pockets of importin β for FG-nucleoporins are differently regulated by RanGTP.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 105: 16101-16106 (2008)
- Kamei, Y., Suzuki, M., Watanabe, K., Fujimoto, K., Kawasaki, T., Deguchi, T., Yoneda, Y., Todo, T., Takagi, S., Funatsu, T. and Yuba, S.Infrared laser-mediated gene induction in targeted single cells in vivo.Nature Methods, 6: 79-81 (2009)
- Katahira, J., Inoue, H., Hurt, E. and Yoneda, Y.Adaptor Aly and co-adaptor Thoc5 function in the Tap-p15-mediated nuclear export of HSP70 mRNA.EMBO J., in press (2009)
(他 21編) |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Copyright (c) 2004-2009, nuclear-dynamics. All Rights Reserved. |
|
|
|
|