9.1¹@ PEG-mediated transformation
Yuji Hiwatashi
Introduction
The capacity to transform a species is a
prerequisite for molecular genetic analysis.¹@
The transformation of P. patens has been
accomplished by both the poly ethylene glycol (PEG)-mediated DNA transfer
method that uses protoplast, and the particle bombardment method.¹@ Electroporation and gene-transfer using
Agrobacterium are a matter of further experiments.¹@ The PEG-mediated DNA transfer method is a most reliable method
for gene-targeting.¹@ In this chapter,
the PEG-mediated DNA transfer into protoplasts is described for stable
transformation.¹@ The transient
transformation using particle bombardment is also introduced
1.
Stable transformation using protoplast and PEG
Foreign DNA is introduced
into protoplasts prepared from propagated protonemata.¹@ Regeneration rate of protoplasts is one of
most critical factors for transformation efficiency.¹@ Protonemata grown for 3-6 days after subculture should be used
for isolating protoplasts.¹@ Older
protonemata may cause a bad transformation efficiency.
5-day-old
protonemal tissue subcultured on cellophane-overlay plates

1-1
Plasmid preparation
[Materials]
QIAGEN Hi-Speed Plasmid
Midi Kit, Promega Wizard Mini-prep Kit, or equivalents.
[procedure]
1. Culture E.coli harboring plasmid DNA.
2. Prepare the plasmid using
QIAGEN Hi-Speed Plasmid Midi Kit or equivalent kit.
3. Digest the plasmid DNA
with adequate restriction enzyme to linearize the plasmid.¹@
4. Purify the digested
plasmid by phenol/chloroform extraction and precipitate with ethanol.
5. Dissolve the plasmid with
TE, adjusting at the concentration of 0.2~1.0 µg/µl.
6. Store at
–30˚C.
1-2
Transformation
We routinely transform
protonemata according to a schedule below.
1. (Day 1) Start
subculturing protonemata at 25˚C for about 4 (3~5) days.
2. (Day 4) Subculture the
propagated protonemata at 25˚C for about 4 (3~5) days.
3. (Day 8~9) Transformation.
It takes 2 days.
4. (Day 12) Incubate 3~5
days.¹@ Transfer top agar containing
regenerating protoplasts onto a selection plate supplemented with antibiotics.¹@ Cultivate more than 3 weeks on the selection
medium.
5. (Day 43; 3 weeks after
TF) Transfer a part of colony grown onto a selection plate to antibiotic-free
plate Incubate more than one week on the non-selection medium.
6. (Day 50; 4 week after TF)
Transfer a part of colony grown on a non-selection plate to selection medium
supplemented with antibiotics.¹@ Incubate
more than one week.¹@¹@
7. (Day 57; 5 weeks after
TF) Select lines surviving on selection medium as stable transformants.
Transformation
(on the First day)
[Materials]
¹E 200 ml flask x 1 (autoclave)
¹E 300 ml flask x 2 (autoclave)
¹E 10 ml pipet x 2 (autoclave)
¹E 50 ml centrifuge tube x 2
(autoclave)
¹E Funnel with a 50 µm nylon mesh
(autoclave)
¹E Forceps x 1 (autoclave)
¹E Cellophane (autoclave)
¹E Yellow for P200 and blue tips for
P1000 (autoclave)
¹E 0.22 µm syringe-driven filter
unit and 10 ml syringe x 2
¹E 0.45 µm syringe-driven filter
unit and 50 ml syringe x 1
¹E Neubauer hemacytometer (Becton
Dickinson no. 424011)
¹E Water bath x 2
¹E Centrifuge
¹E 50 ml conical tube (Falcon, Iwaki,
etc) (sterile)
¹E 15 ml conical tube (Falcon, Iwaki,
etc) (sterile)
¹E 15 ml conical tube (Falcon 2057)
(sterile)
¹E 6-cm Petri dish (sterile)
¹E Parafilm
[Solution]
¹E 500 ml 8% (w/v) mannitol solution
(autoclave)
¹E 2 g PEG6000 in a 10 ml vial and a
small stir bar (autoclave)
¹E 1% (w/v) MES (pH5.6)
¹E 100 ml protoplast liquid medium
(autoclave)¹@¹@¹@
|
H2O |
90 ml |
|
Stock A |
1 ml |
|
Stock B |
1 ml |
|
Stock C |
0.1 ml |
|
5 g/lAmmonium tartrate |
1 ml (50 mg/l) |
|
Mannitol |
6.6 g (6.6%) |
|
Glucose |
0.5 g |
|
|
Fill up to 100 ml with
H2O |
¹E 500 ml 8% (w/v) Mannitol
¹E 1 M Ca(NO3)2
Solution
¹E 1 M MgCl2 Solution
¹E Driselase (We use driselase C-20,
kindly provided by Kyowa Hakko Co., Ltd.)
[procedure]
1. Add 0.5 g of driselase in
a 50 ml conical tube and then add 25 ml of 8% mannitol solution. Mix well.
2. Add 1 ml of 1 M Ca(NO3)2
and 100 µl of 1M Tris-HCl (pH8.0) into 9 ml of 8% (w/v) mannitol solution
and mix. Filter the solution with a 0.22 µm filter.
3. (Preparation of PEG/T)
Add 5 ml of the filtered solution in step (2) to the autoclaved PEG. Dissolve
the PEG completely. This solution is called PEG/T.
4. (Preparation of MMM) Mix
910 mg of mannitol, 0.15 ml of MgCl2, 1 ml of 1% MES (pH5.6) and
8.85 ml of H2O, and then filter the solution with a 0.22 µl
filter.
5. Set water baths at
45˚C and 20˚C.
6. Centrifuge the driselase
solution at 4000 rpm for 5 min.
7. Transfer the supernatant
to a 50 ml syringe with a 0.45 µm filter unit and filter it into a 50 ml
centrifuge tube.
8. Put propagated protonema
(mainly chloronema) into the driselase solution and incubate at 25˚C for
30 min.¹@ Mix gently every 5 min.
¹@
9. Filter the protonemata through
50 µm nylon mesh.
10. ¹@Centrifuge freshly isolated protoplasts at
1000 rpm (180 x g) for 2 min, and suspend gently in 40 ml of 8% (w/v)
mannitol.¹@ Repeat this washing procedure
twice.¹@
 ¹@
¹@ ¹@
¹@
11. ¹@Count finally suspended protoplasts with
hemacytometor, and re-suspend at 1.6 x 106 ml-1 in the MMM
solution.
MMM (ml) = number of
protoplasts per square (large nine squares) x 104 (cell/ml) x 40
(ml) / (1.6 x 106)
 ¹@
¹@
12. ¹@Add 30 µl of plasmid DNA into a 15 ml
conical tube (Falcon 2057). Then, add 300 µl of protoplast suspension and
300 µl of PEG solution to the tube and mix gently.
¹@
13. ¹@Incubate the transformation mixture at 45˚C
for 5 min and then at 20˚C for 10 min.

14. ¹@Dilute the transformation mixture by adding
300 µl of protoplast liquid medium every 3 min at 5 times and then 1 ml
of protoplast liquid medium every 3 min at 5 times.
¹@ ¹@
¹@ ¹@
¹@
15. ¹@Pour the diluted protoplast solution into a 6
cm-dish and incubate at 25˚C overnight in darkness.
¹@ ¹@
¹@
[Key points]
¹E Suspend protoplasts in the MMM
solution by pipetting gently if protoplasts aggregate on the bottom of the
centrifuge tube.¹@
¹E Use 15 ml falcon tube (2057) for
transfer of plasmid.¹@
¹E Keep temperature of a water bath at
20˚C after heat-shock.¹@
Transformation
(on the second day)
[Materials]
¹E 10 ml disposable pipet (sterile) or
white tip for P5000 (autoclave)
¹E Forceps x 1 (autoclave)
¹E Cellophane (autoclave)
¹E 15 ml conical tube (Falcon)
¹E Centrifuge
¹E Surgical tape
[Solution]
¹E PRM/T¹@ Autoclave
|
H2O |
180 ml |
|
Stock B |
2 ml |
|
Stock C |
2 ml |
|
Stock D |
2 ml |
|
Alternative TES |
0.2 ml |
|
500mM Ammoniumtartrate |
2 ml (=5 mM) |
|
Mannitol |
16 g (¹¹8%) |
|
CaCl2 2H2O |
0.29 g (10 mM) |
|
Agar (Sigma: A6924) |
1.6 g |
|
|
Fill up to 200 ml with
H2O |
¹E PRM/B (1000 ml) Autoclave
|
H2O |
900 ml |
|
Stock B |
10 ml |
|
Stock C |
10 ml |
|
Stock D |
10 ml |
|
Alternative TES |
1 ml |
|
500 mM Ammoniumtartrate |
10 ml (= 5 mM) |
|
Mannitol |
60 g (= 6%) |
|
CaCl2 2H2O |
1.47 g (=10 mM) |
|
Agar (Sigma, A6924, Nacalai
Tesque: cat. no. 01028-85) |
8 g (=0.8%) |
|
|
Fill up to 1000 ml with
H2O |
[Procedure]
1. ¹@Overlay a cellophane on a 9 cm-dish
containing PRM/B medium.
2. ¹@Remove the protoplast solution into a 15 ml
conical tube (Falcon 2196) and centrifuge at 1000 rpm (180 x g) for 2min.

3. ¹@Re-suspend the protoplasts in 8 ml of PRM/T
medium by pipetting.
4. ¹@Pour 2 ml of protoplast suspension on a 9
cm-dish containing PRM/B medium overlaid with a cellophane.

5. Incubate the plate at 25˚C
for 3 days under continuous daylight with a light flux of 50 µmol m-2
s-1.¹@
Transfer
to selection medium (4 days after TF)
[Materials]
¹E Forceps x 2 (autoclave)
¹E Surgical tape
[Solution]
¹E Selection medium (BCDAT supplemented
with adequate antibiotics)
|
H2O |
900 ml |
|
Stock B |
10 ml |
|
Stock C |
10 ml |
|
Stock D |
10 ml |
|
Alternative TES |
1 ml |
|
500mM Ammonium tartrate |
10ml (= 5 mM) |
|
50mM CaCl2 2H2O (powder) |
20 ml (= 1 mM) ¹@(0.15 g) |
|
Agar (Sigma; A6924, Nacalai
Tesque: cat. no. 01028-85) |
8 g (= 0.8%) |
|
|
Fill up to 100 ml with
H2O |
After autoclaved, allow
to cool at ~50˚C and add adequate antibiotics into the medium.¹@ Store at 4˚C.
Antibiotics
used for selection
a)
Genetecin (G418)
Invitrogen
(cat.no. 10131-035)¹@ 50 mg/mL solution
Use at the
final concentration of 20 mg/l
b) Hygromycin B
Invitrogen
(cat.no. 10687-010)¹@ 50 mg/ml solution
Use at the
final concentration of 30 mg/l in the medium.
c) Zeocin
Invitrogen
(cat.no. R250-01)¹@ 100 mg/ml solution
Use at the
final concentration of 50 mg/l in the medium.¹@
!NOTE!
Zeocin is light sensitive. Store zeocin solution and
plates or medium containing zeocin in the dark.
d) BS-S
Funakoshi co., Ltd. (cat. no. KK-400)
Use at the final concentration of 75 mg/l in the medium.
1. ¹@Transfer the cellophane attached to cultures
to BCDAT medium supplemented with adequate antibiotics.¹@ .
2. Incubated at 25˚C
for 3~4 weeks under continuous light.¹@
 ¹@A plate after an
incubation of 2 weeks
¹@A plate after an
incubation of 2 weeks
[Key points]
¹E Use plates containing zeocin, which
are freshly prepared.
Transfer
to drug-free medium (after an incubation of 3-4 weeks on selection medium)
[Materials]
¹E Forceps (autoclave)
¹E BCDAT plate
¹E Surgical tape
[Procedure]
1. ¹@Transfer each colony under antibiotic
selection to antibiotic-free BCDAT medium.¹@
2. ¹@Culture at 25˚C for 1 week under
continuous light.
 ¹@A
plate under no selection
¹@A
plate under no selection
[Key points]
¹E Transfer independent colony to the
selection medium to avoid generating a chimerical colony.
¹E Incubate the plate for more than 1
week.
Transfer
to selection medium (after an incubation of 1 week on drug-free medium)
[Materials]
¹E forceps (autoclave)
¹E BCDAT plate containing adequate
antibiotics
¹E Surgical tape
[Procedure]
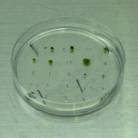
1. ¹@After an incubation of 1 week, re-transfer a
part (protonema) of each transformant to BCDAT medium supplemented with adequate
antibiotics.¹@ Seal the plates with a
surgical tape
2. ¹@After an incubation of 1 week, select transformants
that are able to survive on selection medium as stable transformants.
 ¹@
¹@
[Key points]
¹E Transfer a part (as small as
possible) of protonemata at the edge of a colony to selection medium.¹@ Do not transfer a whole colony or
gametophores.
¹E Use plates containing zeocin, which
are freshly prepared.
¹E Some kinds of disruptants may show
reduced growth.¹@ Do not miss positive
transformants even if growth of colony is reduced.
¹E Note that PEG-mediated transformation will generate polyploid by protoplast fusion.¹@ The colony of polyploid shows different shape (typically more caulonema and few gametophore) from that of wild type.¹@ In this case, estimation of DNA amount using flow cytometry is needed.