11.4
Conditional Deletion
11.4.1
Conditional Knock-out (KO)
Minoru Kubo
Introduction
It is a powerful tool for
characterization of the gene function to analyze a ügloss-of-functionüh
mutant with the deficient gene. Although gene KO (= disruptant) in P. patens has been useful for
loss-of-function analyses, it is important to avoid lethality of gene KO
because the moss is haploid in most of its life cycle. Thus, we developed a
conditional KO system by using Cre-loxP system, in which Cre recombinase is
expressed under the control of HSP facilitating excision of target gene flanked
by loxP sites (Fig.1).
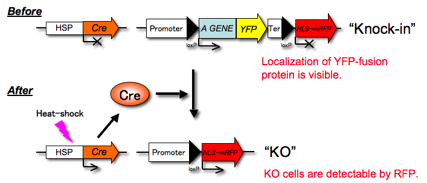
Fig.1 A scheme of
conditional KO. HSP: heat shock
promoter, Cre: Cre recombinase, YFP: yellow fluorescent protein (Citrine),
NLS-mRFP: monomeric red fluorescent protein with nuclear localizing signal.
Materials and methods
How to make a construct
First,
we established the parental line harboring Cre recombinase driven by HSP in P. patens genome (HSP::Cre line). To
make conditional KO construct for the target gene, of which three genomic
regions, 5üfUTR (promoter), CDS (gene) and 3üfUTR are amplified with proof-reading DNA polymerase from P. patens genomic DNA and
directionally inserted at BstZ17I, EcoRV and SmaI in pCKO2, respectively
(Fig.2).
Transformation and selection of candidate lines
The
fragment integrated to P. patens
genome is excised by appropriate restriction enzyme (generally PmeI). The
fragments are transformed to HSP::Cre line by PEG-mediated transformation (see
Chapter 9.1). For detail of transformation and selection of
candidate lines, see Chapter 11.3.
How to induce conditional KO
Transgenic
P. patens harboring constructs of
conditional KO and HSP::Cre are cultured at 25üÄ.
To treat heat-shock, they are transferred to 38üÄ for
1hr and then returned to 25üÄ. To effectively induce KO, you should
carry out this treatment per day twice.
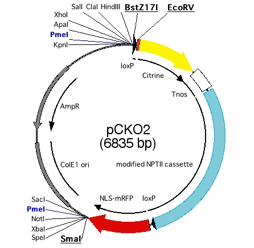
Fig.2 Vector map of
pCKO2.
pCKO2
containing loxP sites for excision by Cre recombinase,ü@ yellow fluorescent protein (Citrine) to fuse
to CDS for detection of subcellular localization, modified NPTII cassette for
transformant selection by G418 and monomeric red florescent protein with
nuclear localization signal (NLS-mRFP) for detection of KO cell. Unfortunately,
NLS-mRFP is not functional. Cut by BstZ17I, EcoRV and SmaI, blunt ends for
ligation of PCR products are generated.
11.4.2
Deletion of a marker gene
Yoshikatsu
Sato
Introduction
In this section,
I introduce the method for the deletion of selection marker gene. The pTN182
(G418 resistant cassette), pTN186 (hygromycin resistant cassette), p35S-zeo
(Zeocin resistant cassette), and pCtrnNPTII2 (G418 resistant cassette for
C-terminal YFP fusion) contain the loxP sites in order to delete the selection
marker gene if needed such as 1) poverty of selection marker cassette for
generating multiple disruptant and 2) restoring the position of 3'UTR of the
target gene.
Method
1. Circular plasmid of pTN75 (Cre recombnase
expression vector + hygromycin resistant cassette) is transiently expressed by
usual PEG transformation method.
2. Cultivate for ~2 weeks on the hygromycin
medium.
3. Inoculate 24 colonies on the BCDAT medium
and cultivate for 2 weeks.
4. (Optional) Confirm the loss of resistance.
Cultivate for 2 weeks on the drug to which the transformed strain showed
tolerant.
5. Confirm deletion of selection marker
cassette by Green-PCR
6. Confirm that the candidate strains are
hygromycin sensitive.
Key point
Circular plasmid of pTN75 should be used so that
efficient expression of Cre recombinase is induced transiently.

Pact: rice actin
promoter
Cre: Cre
recombinase gene
TrbcS: rbcS
terminator
Pcmv: CaMV 35S
promoter
aph4: hygromycin
resistant gene
Tcmv: CaMV 35S
terminator