11.3
Conditional knock down for specific gene by artificial microRNA (amiRNA)
ü@ü@ü@ü@ Chaoyang Cheng, Tetsuya Kurata, and
Mitsuyasu Hasebe
Introduction
ü@ü@ miRNAs are approximately 21 nt small RNAs
which derived from specific MIR gene loci. These miRNAs regulate a target gene
expression through mRNA degradation. Effects of artificially constructed miRNA
on knocking down a target gene have been examined in Arabidopsis and
Physcomitrella (Schwab et al., 2005, 2006; Khraiwesh et al., 2008).
ü@ü@ In this chapter, we describe an inducible
knock-down system combining the advantage of amiRNAs and the inducible
expression method using XVE system (see chapter * in this manual).
References
Schwab
et al.,
Specific
effects of microRNAs on the plant transcriptome.
Dev
Cell 8: 517–527 (2005)
Schwab
et al.,
Highly
specific gene silencing by artificial microRNAs in Arabidopsis.
Plant
Cell 18: 1121–1133 (2006)
Khraiwesh
et al.,
Specific
Gene Silencing by Artificial MicroRNAs in Physcomitrella patens: An Alternative
to Targeted Gene Knockouts
Plant
Physiol. 148: 684-693 (2008)
Materials and Methods
Design for amiRNA
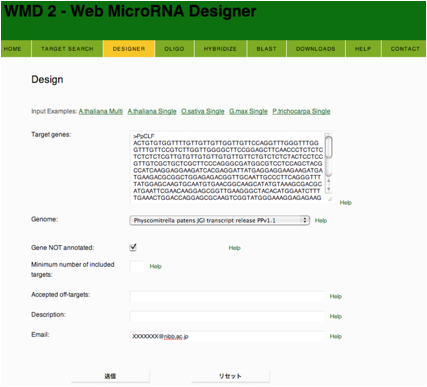
ü@ amiRNA sequences for specific genes were designed
using amiRNA designer web site (WMD2; http://wmd2.weigelworld.org/cgi-bin/mirnatools.pl?page=3). Criteria for selecting
amiRNAüfs sequence are mentioned in this web site.
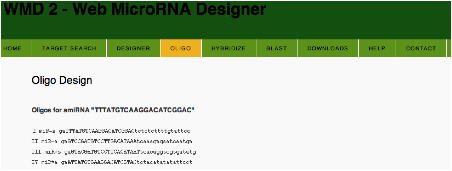
Oligo
primers for PCR are also designed in this web page (see OLIGO button).
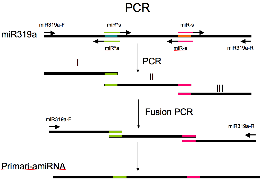
Construction for amiRNA precursor
ü@ For constructing amiRNA precursors, fragment
I, II, and III were amplified using primers hybridizing miR319a
(miR319a-F: CACCACAAACACACGCTCGGACGü@[CACC at the 5' end is for pENTR/D-TOPO] and miR319a-R:
CCTATCCATGGCGATGCC)
and the 4 oligo primers designed above (miR-s~miR*a). PCR enzyme KODplus
(Toyobo) and miR319a precursor fragment plasmid cloned into pRS300 as a
template were used (Schwab et al., 2006). The amplified fragments were
agarose-gel extracted using QIAquick Gel Extraction Kit (QIAGEN) to exclude the
primers and template DNA, and were fused by PCR using the miR319a-F and
–R.
Primary-amiRNA
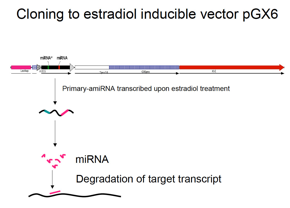
Cloning amiRNA precursor into estradiol
inducible vector pGX6 or pGX8
ü@ Resulted primary-amiRNA fragment was cloned
into pENTR (invitrogen), and sub-coned into pGX6 (or pGX8)-Gateway destination
vector (See chapter * in this manual). The resulted plasmid is digested to
linearize for transformation of Physco.
RT-PCR to examine knock-down of targeted
RNA by induced amiRNA
ü@ Physco transgenic lines expressing amiRNA precursor
were treated by 2uM estradiol for 2 to 9 days, for total RNA extraction and
phenotype observation. Total RNA was extracted with RNAeasy (Qiagen) from the
total tissues (including protonema, gametophore, and rizhoid) at 2 days-treated
moss. 1ug Total RNA was used for reverse transcription using Ready-To-Go You-Prime First-Strand Beads (GE healthcare). Reaction mixtures were diluted
to 5 folds before used for PCR. Primers upstream of the cleavage site were
designed for PCR. We use KODplus (Toyobo) for semi-quantitative RT-PCR, and QuantiTect SYBR Green PCR Kit (QIAGEN) and the 7500 Real Time PCR
system (Applied Biosystme) for quantitative RT-PCR (QRT-PCR). The delat-delta method was
used to calculate the relative difference among sample in QRT-PCR.