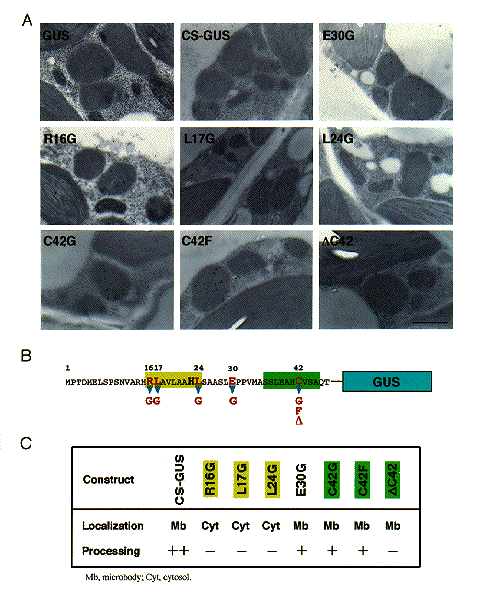
NATIONAL INSITUTE FOR BASIC BIOLOGY
National Institute for Basic Biology
Division of Cell Mechanisms
- Professor:
- Mikio Nishimura
- Associate Professor (adjunct):
- Masayoshi Maeshima
- Research Associates:
- Makoto Hayashi
- Ikuko Hara-Nishimura
- Tomoo Shimada
- Ikuko Hara-Nishimura
- JSPS Postdoctoral Fellow:
- Tetsu Kinoshita
- NIBB Fellow:
- Akira Kato
- Graduate Students:
- Nagako Hiraiwa
- Shoji Mano
- Hiroshi Hayashi
- Kenji Yamada
- Daigo Takemoto1)
- Yuki Tachibe2)
- Shoji Mano
- Technical Staffs:
- Maki Kondo
- Katsushi Yamaguchi
- Monbusho Foreign Scientist:
- Luz Marina Melgarejo3)
- Visiting Scientists:
- Yasuko Koumoto
- Miwa Kuroyanagi
| 1) from Nagoya University |
| 2) from Hiroshima University |
| 3) from Colombia National University |