3.3 Observation of mitosis in a protonemal cell
Yuji Hiwatashi
Introduction
This protocol
gives you the opportunity to observe cell divisions of protonemal apical
cells.
Procedure
(1) Pre-culture
1. Sub-culture
protonemata on cellophane-overlaid BCDATG* plates under continuous white light
(30-40 µmol m-2 sec-1) at 25˚C every 5~7 days.
2. Inoculate
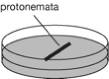
~7-day-old protonema tissue on BCDATG plates (3 cm-diameter dish) and cover
them with a sterile cover slip (18 x18 mm). Place protonema tissue in a line
(figure).
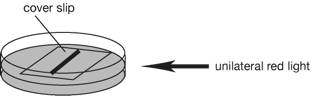
3. Incubate the
plates under unilateral red light (15-20 µmol m-2 sec-1) at 25˚C for
7 days. Cover a fluorescent tube light
with a red plastic sheet, and use as a red light (red plastic sheet: shikolite
102; Mitsubishi Rayon, Japan, http://www.mrc.co.jp/shinkolite/index.html). New
protonema grow to the direction of the red light.
(2)
Time-lapse observation
1. Keep room
temperature at 25C.
2. Remove the
cover slip from the plate and cut an agar block containing protonemata with a
scalpel.
3. Place the
agar block up-side down in a 35 mm glass-bottom dish (IWAKI 3910-039: a 27 mm diameter opening in the center of a dish, http://www.atgc.co.jp/div/rika/hbine/index_e.html), and
protonemata attach to the bottom of the dish.
Seal the dish with parafilm.
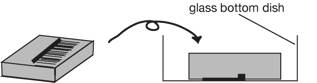
4. Place the dish on a stage of an inverted microscope.
5. Seek a
protonemal apical cell just before cell division and focus its nucleus. The
apical cell before cell division is much longer than its neighboring subapical
cell and its cytoplasm is localized to more apical end. One of the signs of mitosis
is a transition of a nuclear shape. Just before entering prophase, a nucleus becomes
spherical rather than oval.
6. Carry out
the time-lapse observation. Mitosis ends within ~30 min in this condition, and
take an image at every 60 sec. Emission light should be as weak as possible
especially when GFP signals are observed. Strong light inhibits cell division
and fades GFP fluorescence.
Solution required
・ BCDATG
1 stock
solutions
solution A (x
100 )
|
Ca(NO3)2·4H2O |
118 g |
|
FeSO4·7H2O |
1.25 g |
|
H2O |
fill up to
1000 ml |
SolutionB (x
100 )
|
MgSO4·7H2O |
25 g |
|
H2O |
fill up to
1000 ml |
Autoclaved
SolutionC (x
100 )
|
KH2PO4 |
25 g |
|
|
adjust pH
to 6.5 with 4 M KOH |
|
H2O |
fill up to
1000 ml |
Autoclaved
Solution D (x
100)
|
KNO3 |
101 g |
|
FeSO4·7H2O |
1.25 g |
|
H2O |
fill up to
1000 ml |
Alternative
TES (x 1000)
|
CuSO4·5H2O |
55 mg |
|
H3BO3 |
614 mg |
|
CoCl2·6H2O |
55 mg |
|
Na2MoO4·2H2O |
25 mg |
|
ZnSO4·7H2O |
55 mg |
|
MnCl2·4H2O |
389 mg |
|
KI |
28 mg |
|
H2O |
fill up to
1000 ml |
Autoclaved
500mM
Ammonium Tartrate (x 100 )
|
Ammonium
Tartrate |
92.05 g |
|
H2O |
fill up to
1000 ml |
Autoclaved
50mM CaCl2 (x
50 )
|
CaCl2·2H2O |
7.35 g |
|
H2O |
fill up to
1000 ml |
Autoclaved
2.BCDATG
|
H2O |
900 ml |
|
Stock B |
10 ml |
|
Stock C |
10 ml |
|
Stock D |
10 ml |
|
Alternative
TES |
1 ml |
|
500mM Ammonium
tartrate |
10ml (= 5
mM) |
|
50mM CaCl2
2H2O (powder) |
20 ml (= 1
mM) (0.15 g) |
|
Glucose |
5 g |
|
Agar (Sigma,
A6924) |
8 g (= 0.8%) |
|
|
Fill up to
1000 mL with H2O |
Autoclaved