14.
Physcomitrella genome project
Tomomichi Fujita, Tomoaki Nishiyama, Takako Tanahashi, and
Mitsuyasu Hasebe
(1)
whole genome sequence
The whole
genome shotgun project of approximately 2,000 Mb corresponding to eight times
of Physcomitrella patens subsp. patens Glansden2004 nuclear
genome is on going under the Community Sequencing Program at the Joint Genome
Institute of U.S. Department of Energy. All DNA sequences will be finished in
2005, and all sequence data are released to public database simultaneously with
sequencing. The genome is expected to be annotated in 2006 together with data
on EST, full-length cDNA sequences, 5' SAGE sequences, and BAC end sequences.
All sequence data are searchable by the BLAST program in PHYSCObase
(http://moss.nibb.ac.jp).
(2)
EST data
EST analyses
of the following five full-length cDNA libraries were performed and all ESTs
are deposited in public DNA databases.
(1) Untreated
protonemata library (9,944 5'ESTs; 9,352 3'ESTs)
(2)
Auxin-treated library (16,733 5'ESTs; 16,763 3'ESTs)
(3)
cytokinin-treated library (16,450 5'ESTs; 15,000 3'ESTs)
(4) Library for protoplasts during the first cell division
(10,535 5'ESTs; 10,975 3'ESTs)
(5)
Library for sporophytes before meiosis with surrounding archegonia (8,514
5'ESTs: 8,241 3'ESTs)
Together
with other 18,686 mRNA sequences deposited in GenBank, total 142,182 ESTs are
open in public DNA databases. These ESTs are assembled into 27,546 sequences
(14,969 contigs and 12,577 singlets).
All clones corresponding to the ESTs
in the five full-length cDNA libraries are distributed from RIKEN Bio Resource
Center (http://www.brc.riken.jp/lab/epd/Eng/index.shtml). Available clones are
searchable in PHYSCObase (http://moss.nibb.ac.jp).
(3)
Full-length cDNA libraries
The following libraries will be
distributed from RIKEN Bio Resource Center (http://www.brc.riken.jp/inf/en/).
(1)
Untreated protonemata library:
Physcomitrella
patens (Hedw.) Bruch & Schimp subsp. patens
collected in Gransden Wood, Huntingdonshire, UK, was used as the wild-type strain.
The protonemata were ground with the Polytron (Kinematica, Littau,
Switzerland), and inoculated in BCDATG medium at 25°C under continuous light,
and the tissues were harvested at the 13 and 14th days. The collected tissue
contained protonemata and young gametophores with two to five leaves. Full-length
cDNA was recovered by using the biotinylated CAP trapper method and the
single-strand linker ligation method were used in the construction of the cDNA
libraries. Clones originated from this library are designated as “pph” clones. >90%
of clones that should have a complete open reading frame. Full-length cDNAs
were cloned into a vector in Fig. 1, which have a pBluescriptII backbore with
Amp resistance.
(2)
Auxin-treated library:
Protonemata
were ground with the Polytron and inoculated into BCD medium that contained 1.0
mM CaCl2 and 1.0 mM NAA (naphthalene acetic acid; Sigma-Aldrich, St.
Louis, MO) at 25°C under continuous light, and the tissues were harvested at
the 8 to 11th days. The collected NAA-treated tissue contained chloronemata,
caulonemata, and rhizoid-like protonemata. Full-length cDNA was recovered by
using the biotinylated CAP trapper method and the single-strand linker ligation
method were used in the construction of the cDNA libraries. One round of
normalization was performed. Clones originated from this library are designated
as “pphn” clones. >90% of clones that should have a complete open reading
frame. Full-length cDNAs were cloned
into a vector in Fig. 1, which have a pBluescriptII backbore with Amp
resistance.
(3)
Cytokinine-treated library:
Protonemata
were ground with the Polytron and inoculated into BCD medium that contained 1.0
mM CaCl2 and 0.50 mM BA (6-benzylaminopurine; Sigma-Aldrich) for the
BA-treated specimensat 25°C under continuous light, and the tissues were
harvested at the 8 to 13the days. The collected BA-treated tissue contained
chloronemata, caulonemata, and malformed buds. Full-length cDNA was recovered
by using the biotinylated CAP trapper method and the single-strand linker
ligation method were used in the construction of the cDNA libraries. One round
of normalization was performed. Clones originated from this library are
designated as “pphb” clones. >90% of clones that should have a complete open
reading frame. Full-length cDNAs were
cloned into a vector in Fig. 1, which have a pBluescriptII backbore with Amp
resistance.
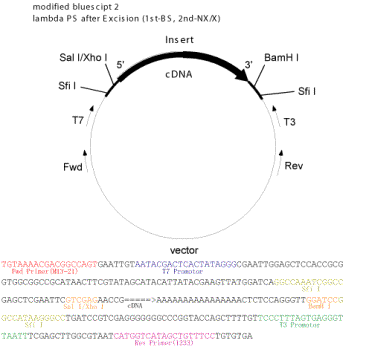
Fig. 1 A vector used for full-length cDNA libraries.
(4)
Library for protoplasts at a stage of the first cell division:
Protonemata
were subcultured into BCDATG medium every ca. 5 days and protoplasts were
prepared. Isolated protoplasts were incubated at 25°C under continuous light for
2-3 days, when the number of cells at a stage of the first cell division, which
is asymmetric, or cells with protrusion are increased. Full-length cDNA was
recovered by Vector-Capping method (Kato et al. (2005) DNA Res. 12:53-62). Clones
originated from this library are designated as “pphf” clones. Full-length cDNAs
were cloned into pGCAPzf3 vector (Fig. 2).
5’....GCCAGGGTTTTCCCAGTCACGACGTTGTAAAACGACGGCCAGTGAA
M13 Forward Primer
T7
Transcription Start
![]()
![]()
AATTTGAATTGTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGCGAATTGGCGGCCAAATCGGCC
T7 promoter SfiI
GAATT( cDNA )GGCCATAAGGGCCAGCTTGAG
SfiI
SP6
Transcription Start
![]()
TATTCTATAGTGTCACCTAAATAGCTTGGCGTAATCATGGTCATAGCTGTTTC
SP6 promoter M13 Reverse
Primer
CTGTGTGAAATTGTTATCCGCTCACAATTCCACACAACATACGAGC....3’
Fig.
2 pGCAPzf3 Vector promoter and cloning
site sequence
(5)Library
for sporophytes before meiosis with surrounding archegonia:
Mosses
were grown on Jiffy 7 for 4-6 weeks at 25℃ (24L) followed 3-4 weeks at 15℃ (8L16D). Sporophytes
before meiosis together with surrounding archegonia were collected under
stereomicroscope. Full-length cDNA was
recovered by using the oligo-capping method (Maruyama and Sugano, 1994, Gene
38: 7-74). Clones originated from this library are designated as “ppsp” clones.
Full-length cDNAs were cloned into pME18S-FL3 vector (AB009864) in Fig. 3.
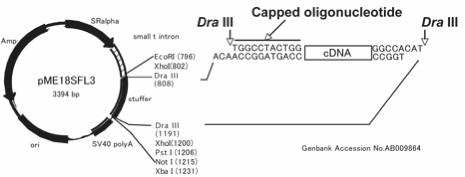
Fig.
3 pME18S-FL3 vector
Reference
T. Nishiyama, T. Fujita, T. Shin-I, M. Seki, H. Nishide, I.
Uchiyama, A. Kamiya, P. Carninci, Y. Hayashizaki, K. Shinozaki, Y. Kohara, M.
Hasebe, Comparative genomics of the Physcomitrella gametophytic transcriptome
and Arabidopsis genome: implication for the land plant evolution. PNAS.100,
8007-8012 (2003)
T.
Fujita, T. Nishiyama, Y. Hiwatashi, and M. Hasebe, Gene tagging, Gene- and
Enhancer-trapping, and Full-length cDNA Overexpression in Physcomitrella
patens. In New
Frontiers in Bryology: Physiology, Molecular Biology, and Functional Genomics.
A. J. Wood, M. J. Oliver, and D. J. Cove eds. Kluwer Academic Publishers,
Dordrecht, Netherlands, pp. 111-132 (2004)